รายชื่อจักรวรรดิเรียงตามพื้นที่
จักรวรรดิอาณานิคมยุโรป[แก้]
เป็นจักรวรรดิสากลที่มาจากยุโรป โดยเริ่มจากโปรตุเกสและสเปนในศตวรรษที่ 15
-
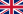
ปี 1920 ดินแดนของจักรวรรดิอังกฤษ (สีแดง) และจักรวรรดิฝรั่งเศส (สีฟ้า)
-
แผนที่ของ จักรวรรดิโปรตุเกส
-
แผนที่ของ จักรวรรดิสเปน
-
แผนที่ของ จักรวรรดิดัตช์
-
แผนที่ของ จักรวรรดิบริติช
-
แผนที่ของ จักรวรรดิฝรั่งเศส
-
แผนที่ของจักรวรรดิเยอรมันในปี 1914
-
แผนที่ของจักรวรรดิอาณานิคมอิตาลีในปี 1939
-
แผนที่ของจักรวรรดิรัสเซียในปี 1866
จักรวรรดิดูตามพื้นที่และประชากร[แก้]
พื้นที่และดินแดนทั้งหมดที่อยู่ในจักรวรรดิ[แก้]
| จักรวรรดิ | พื้นที่ใหญ่ที่สุด | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ล้าน กม2 | ล้าน ตารางไมล์ | % ของโลก | ปี | |
| จักรวรรดิบริติช[a] | 35.5[1] | 13.71 | 26.35% | 1920[1] |
| จักรวรรดิมองโกล[b] | 24.0[1][2] | 9.27 | 17.81% | 1270[2] หรือ 1309[1] |
| จักรวรรดิรัสเซีย[c] | 22.8[1][2] | 8.80 | 16.92% | 1895[1][2] |
| ราชวงศ์ชิง[d] | 14.7[1][2] | 5.68 | 10.91% | 1790[1][2] |
| จักรวรรดิสเปน | 13.7[1] | 5.29 | 10.17% | 1810[1] |
| จักรวรรดิอาณานิคมฝรั่งเศสที่สอง | 11.5[1] | 4.44 | 8.53% | 1920[1] |
| รัฐเคาะลีฟะฮ์อับบาซียะฮ์ | 11.1[1] | 4.29 | 8.24% | 750[1] |
| รัฐเคาะลีฟะฮ์อุมัยยะฮ์ | 11.1[1] | 4.29 | 8.24% | 720[1] |
| ราชวงศ์หยวน | 11.0[1] | 4.25 | 8.16% | 1310[1] |
| จักรวรรดิซฺยงหนู | 9.0[2][3] | 3.47 | 6.68% | 176 BC[2][3] |
| จักรวรรดิบราซิล[e] | 8.337[4] | 3.22 | 6.19% | 1889[4] |
| จักรวรรดิญี่ปุ่น | 7.4[5]–8.51 | 2.86–3.285[6] | 5.49%–6.32% | 1942[5][6] |
| สหภาพไอบีเรีย | 7.1[1] | 2.74 | 5.27% | 1640[1] |
| ราชวงศ์ฮั่นตะวันออก | 6.5[3] | 2.51 | 4.82% | 100[3] |
| ราชวงศ์หมิง | 6.5[1][2] | 2.51 | 4.82% | 1450[1][2] |
| รัฐเคาะลีฟะฮ์รอชิดูน | 6.4[1] | 2.47 | 4.75% | 655[1] |
| First Turkic Khaganate | 6.0[2][3] | 2.32 | 4.45% | 557[2][3] |
| อาณาจักรข่านแห่งโกลเดนฮอร์ด | 6.0[1][2] | 2.32 | 4.45% | 1310[1][2] |
| ราชวงศ์ฮั่นตะวันตก | 6.0[2][3] | 2.32 | 4.45% | 50 BC[2][3] |
| จักรวรรดิอะคีเมนิด | 5.5[2][3] | 2.12 | 4.08% | 500 BC[2][3] |
| จักรวรรดิโปรตุเกสที่สอง[e] | 5.5[1] | 2.12 | 4.08% | 1820[1] |
| ราชวงศ์ถัง | 5.4[1][2] | 2.08 | 4.01% | 715[1][2] |
| ราชอาณาจักรมาเกโดนีอา | 5.2[2][3] | 2.01 | 3.86% | 323 BC[2][3] |
| จักรวรรดิออตโตมัน | 5.2[1][2] | 2.01 | 3.86% | 1683[1][2] |
| ราชวงศ์หยวนเหนือ | 5.0[1] | 1.93 | 3.71% | 1368[1] |
| จักรวรรดิโรมัน | 5.0[2][3] | 1.93 | 3.71% | 117[2][3] |
| ราชวงศ์ซิน | 4.7[3] | 1.81 | 3.49% | 10[3] |
| จักรวรรดิทิเบต | 4.6[1][2] | 1.78 | 3.41% | 800[1][2] |
| Xianbei state | 4.5[7] | 1.74 | 3.34% | 200[7] |
| จักรวรรดิเม็กซิโกที่หนึ่ง | 4.429[8] | 1.71 | 3.29% | 1821[8] |
| ราชวงศ์เตมือร์ | 4.4[1][2] | 1.70 | 3.27% | 1405[1][2] |
| รัฐเคาะลีฟะฮ์ฟาฏิมียะฮ์ | 4.1[1][2] | 1.58 | 3.04% | 969[1][2] |
| Eastern Turkic Khaganate | 4.0[3] | 1.54 | 2.97% | 624[3] |
| ราชวงศ์ฮั่น | 4.0[2][3] | 1.54 | 2.97% | 441[2][3] |
| จักรวรรดิโมกุล | 4.0[1][2] | 1.54 | 2.97% | 1690[1][2] |
| จักรวรรดิเซลจุค | 3.9[1][2] | 1.51 | 2.89% | 1080[1][2] |
| จักรวรรดิซิลูซิด | 3.9[2][3] | 1.51 | 2.89% | 301 BC[2][3] |
| จักรวรรดิอิตาลี | 3.825[9] | 1.48 | 2.84% | 1941[9] |
| จักรวรรดิข่านอิล | 3.75[1][2] | 1.45 | 2.78% | 1310[1][2] |
| รัฐข่านซูงการ์ | 3.6[7] | 1.39 | 2.67% | 1650[7] |
| จักรวรรดิข่านชากาทาย | 3.5[1][2] | 1.35 | 2.60% | 1310[1] or 1350[1][2] |
| จักรวรรดิซาเซเนียน | 3.5[2][3] | 1.35 | 2.60% | 550[2][3] |
| Western Turkic Khaganate | 3.5[3] | 1.35 | 2.60% | 630[3] |
| จักรวรรดิซฺยงหนูตะวันตก | 3.5[3] | 1.35 | 2.60% | 20[3] |
| จักรวรรดิอาณานิคมฝรั่งเศสที่หนึ่ง | 3.4[1] | 1.31 | 2.52% | 1670[1] |
| จักรวรรดิกาสนาวิยะห์ | 3.4[1][2] | 1.31 | 2.52% | 1029[1][2] |
| ราชวงศ์โมริยะ | 3.4[3]–5.0[2] | 1.31–1.93 | 2.52%–3.71% | 261 BC[3] or 250 BC[2] |
| Delhi Sultanate | 3.2[1][2] | 1.24 | 2.37% | 1312[1][2] |
| จักรวรรดิอาณานิคมเยอรมัน | 3.147 | 1.215[10] | 2.34% | 1911[10] |
| Northern Song dynasty | 3.1[1][2] | 1.20 | 2.30% | 980[1][2] |
| Uyghur Khaganate | 3.1[1][2] | 1.20 | 2.30% | 800[1][2] |
| ราชวงศ์จิ้นตะวันตก | 3.1[3] | 1.20 | 2.30% | 280[3] |
| จักรวรรดิเดนมาร์ก | 3.0[11] | 1.16 | 2.23% | 1700[11] |
| ราชวงศ์สุย | 3.0[3] | 1.16 | 2.23% | 589[3] |
| Safavid empire | 2.9[7] | 1.12 | 2.15% | 1630[7] |
| Samanid Empire | 2.85[1][2] | 1.10 | 2.12% | 928[1][2] |
| ราชวงศ์จิ้นตะวันออก | 2.8[3] | 1.08 | 2.08% | 347[3] |
| Median Empire[f] | 2.8[2][3] | 1.08 | 2.08% | 585 BC[2][3] |
| จักรวรรดิพาร์เธีย | 2.8[2][3] | 1.08 | 2.08% | 1[2][3] |
| Rouran Khaganate | 2.8[2][3] | 1.08 | 2.08% | 405[2][3] |
| จักรวรรดิไบแซนไทน์ | 2.7[2]–2.8[3] | 1.04–1.08 | 2.00%–2.08% | 555[2] or 450[3] |
| อาณาจักรอินโด-ไซเทีย | 2.6[3] | 1.00 | 1.93% | 20[3] |
| ราชวงศ์เหลียว | 2.6[1][2] | 1.00 | 1.93% | 947[1][2] |
| Greco-Bactrian Kingdom | 2.5[3] | 0.97 | 1.86% | 184 BC[3] |
| Later Zhao | 2.5[3] | 0.97 | 1.86% | 329[3] |
| จักรวรรดิมราฐา | 2.5[2] | 0.97 | 1.86% | 1760[2] |
| จักรวรรดิอาณานิคมเบลเยียม | 2.366[9]–2.47 | 0.91–0.95[13] | 1.76%–1.83% | 1941[9] or 1939[13] |
| ราชวงศ์จิน | 2.3[1][2] | 0.89 | 1.71% | 1126[1][2] |
| Khwarazmian Empire | 2.3[2]–3.6[1] | 0.89–1.39 | 1.71%–2.67% | 1210[2] or 1218[1] |
| ราชวงศ์ฉิน | 2.3[3] | 0.89 | 1.71% | 220 BC[3] |
| จักรวรรดิดัตช์ | 2.1[7] | 0.81 | 1.56% | 1938[7] |
| จักรวรรดิฝรั่งเศสที่หนึ่ง | 2.1[1] | 0.81 | 1.56% | 1813[1] |
| จักรวรรดิรุสเคียฟ | 2.1[1][2] | 0.81 | 1.56% | 1000[1][2] |
| รัฐสุลต่านมัมลูก | 2.1[1][2] | 0.81 | 1.56% | 1300[1] or 1400[2] |
| ราชวงศ์ซ่งใต้ | 2.1[1] | 0.81 | 1.56% | 1127[1] |
| จักรวรรดิโปรตุเกสที่สาม | 2.1[1] | 0.81 | 1.56% | 1900[1] |
| Almohad Caliphate | 2.0[2]–2.3[1] | 0.77–0.89 | 1.48%–1.71% | 1200[2] or 1150[1] |
| วุยก๊ก | 2.0[3] | 0.77 | 1.48% | 263[3] |
| เฉียนฉิน | 2.0[3] | 0.77 | 1.48% | 376[3] |
| Former Zhao | 2.0[3] | 0.77 | 1.48% | 316[3] |
| Ghurid dynasty | 2.0[7] | 0.77 | 1.48% | 1200[7] |
| จักรวรรดิอินคา | 2.0[1][2] | 0.77 | 1.48% | 1527[1][2] |
| จักรวรรดิกุษาณะ | 2.0[2]–2.5[3] | 0.77–0.97 | 1.48%–1.86% | 200[2][3] |
| ราชวงศ์หลิวซ่ง | 2.0[3] | 0.77 | 1.48% | 450[3] |
| ราชวงศ์เว่ย์เหนือ | 2.0[3] | 0.77 | 1.48% | 450[3] |
| จักรวรรดิโรมันตะวันตก | 2.0[3] | 0.77 | 1.48% | 395[3] |
| Ayyubid dynasty | 1.7[1]–2.0[2] | 0.66–0.77 | 1.26%–1.48% | 1200[1] or 1190[2] |
| จักรวรรดิคุปตะ | 1.7[3]–3.5[2] | 0.66–1.35 | 1.26%–2.60% | 440[3] or 400[2] |
| Hephthalite Empire | 1.7[14]–4.0[3] | 0.66–1.54 | 1.26%–2.97% | 500[14] or 470[3] |
| Buyid dynasty | 1.6[1][2] | 0.62 | 1.19% | 980[1][2] |
| ง่อก๊ก | 1.5[3] | 0.58 | 1.11% | 221[3] |
| ราชวงศ์ฉีเหนือ | 1.5[3] | 0.58 | 1.11% | 557[3] |
| จักรวรรดิซฺยงหนูเหนือ | 1.5[3] | 0.58 | 1.11% | 60[3] |
| ราชวงศ์โจวเหนือ | 1.5[3] | 0.58 | 1.11% | 577[3] |
| จักรวรรดิอัสซีเรียใหม่ | 1.4[2][15] | 0.54 | 1.04% | 670 BC[2][15] |
| ราชวงศ์โมริยะตะวันออก | 1.3[3] | 0.50 | 0.96% | 210 BC[3] |
| ราชวงศ์เหลียง | 1.3[2][3] | 0.50 | 0.96% | 502,[3] 549,[3] or 579[2] |
| อิหร่านกอญัร | 1.29 | 0.50[16] | 0.96% | 1873[16] |
| อาณาจักรอักซุม | 1.25[2] | 0.48 | 0.93% | 350[2] |
| ราชวงศ์ชาง | 1.25[2][15] | 0.48 | 0.93% | 1122 BC[2][15] |
| ฟรังเกีย | 1.2[1][2] | 0.46 | 0.89% | 814[1][2] |
| อาณาจักรศรีวิชัย | 1.2[2] | 0.46 | 0.89% | 1200[2] |
| อาณาจักรอินโด-กรีก | 1.1[3] | 0.42 | 0.82% | 150 BC[3] |
| จักรวรรดิมาลี | 1.1[1][2] | 0.42 | 0.82% | 1380[1][2] |
| เครือจักรภพโปแลนด์–ลิทัวเนีย | 1.1[1][2] | 0.42 | 0.82% | 1480[2] or 1650[1] |
| Almoravid dynasty | 1.0[2] | 0.39 | 0.74% | 1120[2] |
| จักรวรรดิหรรษ | 1.0[1][2] | 0.39 | 0.74% | 625[1] or 648[1][2] |
| Gurjara-Pratihara dynasty | 1.0[1] | 0.39 | 0.74% | 860[1] |
| จักรวรรดิโรมันอันศักดิ์สิทธิ์ | 1.0[1] | 0.39 | 0.74% | 1050[1] |
| Khazar Khanate | 1.0[1]–3.0[2] | 0.39–1.16 | 0.74%–2.23% | 900[1] or 850[2] |
| จักรวรรดิเขมร | 1.0[1][2] | 0.39 | 0.74% | 1290[1][2] |
| จักรวรรดิอียิปต์ | 1.0[2][15] | 0.39 | 0.74% | 1450 BC[15] or 1300 BC[2] |
| ราชอาณาจักรทอเลมี | 1.0[3] | 0.39 | 0.74% | 301 BC[3] |
| Qara Khitai | 1.0[1]–1.5[2] | 0.39–0.58 | 0.74%–1.11% | 1130[1] or 1210[2] |
| Scythia | 1.0[14] | 0.39 | 0.74% | 400 BC[14] |
| จ๊กก๊ก | 1.0[3] | 0.39 | 0.74% | 221[3] |
| Tahirid dynasty | 1.0[1] | 0.39 | 0.74% | 800[1] |
| เซี่ยตะวันตก | 1.0[2] | 0.39 | 0.74% | 1100[2] |
| จักรวรรดิสวีเดน | 0.99[17] | 0.38 | 0.73% | 1700[17] |
| นาซีเยอรมนี | 0.824[9] | 0.32 | 0.61% | 1941[9] |
| จักรวรรดิแอกแคด | 0.8[15] | 0.31 | 0.59% | 2250 BC[15] |
| อาวาร์ยูเรเชีย | 0.8[3] | 0.31 | 0.59% | 600[3] |
| ฉู่ | 0.8[3] | 0.31 | 0.59% | 300 BC[3] |
| ฮัน | 0.8[3] | 0.31 | 0.59% | 287[3] |
| จักรวรรดิซองไฮ | 0.8[1] | 0.31 | 0.59% | 1550[1] |
| ฮิกซอส | 0.65[15] | 0.25 | 0.48% | 1650 BC[15] |
| Twenty-sixth Dynasty of Egypt | 0.65[15] | 0.25 | 0.48% | 550 BC[15] |
| Rozvi Empire | 0.624[18] | 0.24 | 0.46% | 1700[18] |
| จักรวรรดิออสเตรีย-ฮังการี | 0.62 | 0.24[19] | 0.46% | 1905[19] |
| รัฐเคาะลีฟะฮ์กุรฏุบะ | 0.6[1] | 0.23 | 0.45% | 1000[1] |
| จักรวรรดิโปรตุเกสที่หนึ่ง | 0.6[1] | 0.23 | 0.45% | 1580[1] |
| ราชอาณาจักรวิซิกอท | 0.6[3] | 0.23 | 0.45% | 580[3] |
| ราชวงศ์โจว | 0.55[20] | 0.21 | 0.41% | 1100 BC[20] |
| จักรวรรดิซิกข์ | 0.52 | 0.20[21] | 0.39% | 1839[21] |
| รัฐเคาะลีฟะฮ์กุรฏุบะ | 0.5[1] | 0.19 | 0.37% | 756[1] |
| โกศล | 0.5[3] | 0.19 | 0.37% | 543 BC[3] |
| ลิเดีย | 0.5[15] | 0.19 | 0.37% | 585 BC[15] |
| แคว้นมคธ | 0.5[3] | 0.19 | 0.37% | 510 BC[3] |
| Middle Kingdom of Egypt | 0.5[15] | 0.19 | 0.37% | 1850 BC[15] |
| Neo-Babylonian Empire | 0.5[15] | 0.19 | 0.37% | 562 BC[15] |
| ราชวงศ์สาตวาหนะ | 0.5[3] | 0.19 | 0.37% | 150[3] |
| ราชวงศ์ที่ยี่สิบห้าแห่งอียิปต์ | 0.5[15] | 0.19 | 0.37% | 715 BC[15] |
| Western Satraps | 0.5[3] | 0.19 | 0.37% | 100[3] |
| อาณาจักรฮิตไทต์ใหม่ | 0.45[15] | 0.17 | 0.33% | 1250 BC–1220 BC[15] |
| ราชวงศ์เซี่ย | 0.45[15] | 0.17 | 0.33% | 1800 BC[15] |
| จักรวรรดิบัลแกเรีย | 0.4[22] | 0.15 | 0.30% | 850[22] |
| ฝรั่งเศสสมัยกลาง | 0.4[1] | 0.15 | 0.30% | 1250[1] |
| Middle Assyrian Empire | 0.4[15] | 0.15 | 0.30% | 1080 BC[15] |
| Old Kingdom of Egypt | 0.4[15] | 0.15 | 0.30% | 2400 BC[15] |
| Sokoto Caliphate | 0.4[23] | 0.15 | 0.30% | 1804[23] |
| จักรวรรดิละติน | 0.35[3] | 0.14 | 0.26% | 1204[3] |
| Ancient Carthage | 0.3[3] | 0.12 | 0.22% | 220 BC[3] |
| อารยธรรมลุ่มแม่น้ำสินธุ | 0.3[20] | 0.12 | 0.22% | 1800 BC[20] |
| Mitanni | 0.3[15] | 0.12 | 0.22% | 1450 BC–1375 BC[15] |
| Ashanti Empire | 0.25[24] | 0.10 | 0.19% | 1820[24] |
| First Babylonian Empire | 0.25[15] | 0.10 | 0.19% | 1690 BC[15] |
| จักรวรรดิแอซเท็ก | 0.22[1] | 0.08 | 0.16% | 1520[1] |
| Zulu Empire | 0.21 | 0.08[25] | 0.16% | 1822[25] |
| จักรวรรดิเอลาไมท์ | 0.2[15] | 0.08 | 0.15% | 1160 BC[15] |
| Phrygia | 0.2[15] | 0.08 | 0.15% | 750 BC[15] |
| Second Dynasty of Isin | 0.2[15] | 0.08 | 0.15% | 1130 BC[15] |
| Urartu | 0.2[15] | 0.08 | 0.15% | 800 BC[15] |
| ราชวงศ์โจวตะวันออก | 0.15[15] | 0.06 | 0.11% | 770 BC[15] |
| อาณาจักรฮิตไทต์กลาง | 0.15[15] | 0.06 | 0.11% | 1450 BC[15] |
| Old Assyrian Empire | 0.15[15] | 0.06 | 0.11% | 1730 BC[15] |
| อาณาจักรฮิตไทต์เก่า | 0.15[15] | 0.06 | 0.11% | 1530 BC[15] |
| Oyo Empire | 0.15[26] | 0.06 | 0.11% | 1680[26] |
| Bornu Empire | 0.13 | 0.05[27] | 0.10% | 1892[27] |
| Larsa | 0.1[15] | 0.04 | 0.07% | 1750 BC–1700 BC[15] |
| Neo-Sumerian Empire | 0.1[15] | 0.04 | 0.07% | 2000 BC[15] |
| Tarascan empire | 0.075[28] | 0.03 | 0.06% | 1450[28] |
| Lagash | 0.05[20] | 0.02 | 0.04% | 2400 BC[20] |
| ซูเมอร์ | 0.05[15] | 0.02 | 0.04% | 2400 BC[15] |
| ||||
แผนที่[แก้]
จักรวรรดิสมัยโบราณ[แก้]
-
จักรวรรดิอะคีเมนิด (จักรวรรดิเปอร์เซีย) 480 ปีก่อนคริสต์ศักราช
-
จักรวรรดิโมริยะ 265 ปีก่อนคริสต์ศักราช
-
ราชวงศ์ฉิน 210 ปีก่อนคริสต์ศักราช
-
จักรวรรดิอาร์เมเนียน 83-69 ปีก่อนคริสต์ศักราช
-
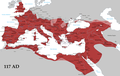
จักรวรรดิโรมันยุคที่รุ่งเรืองสูงสุด ในปีคริสต์ศักราช 117
จักรวรรดิสมัยกลาง[แก้]
-
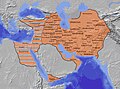
จักรวรรดิมองโกล ช่วงรุ่งเรืองสูงสุด
-
จักรวรรดินอร์เวย์ช่วงรุ่งเรืองสูงสุด(รวมกรีนแลนด์)
-
ช่วงรุ่งเรืองสูงสุดของรัฐเคาะลีฟะฮ์.ขยายตัวภายใต้ศาสดามูฮัมหมัด, 622-632การขยายตัวในช่วงจักรวรรดิรอชิดีน, 632-661การขยายตัวในช่วงราชวงศ์อุมัยยะฮ์, 661-750
-
ภาพเคลื่อนไหวแสดงดินแดนภายใต้ราชวงศ์ถัง
-
จักรวรรดิแซสซานิด ช่วงรุ่งเรืองสูงสุด
จักรวรรดิสมัยใหม่[แก้]
-
อาณานิคมที่ครั้งหนึ่งเคยเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของจักรวรรดิบริติช
-
จักรวรรดิรัสเซีย ช่วงรุ่งเรืองสูงสุด
-
แผนที่ของจักรวรรดิสเปน
-
แผนที่ของจักรวรรดิดัตช์
-
แผนที่ของจักรวรรดิอิตาลี ในปี 1939
-
ดินแดนและขอบเขตอำนาจของจักรวรรดิอาณานิคมฝรั่งเศส
-
แผนที่ของจักรวรรดิอาณานิคมเยอรมัน ในปี 1914
-
นาซีเยอรมนี ช่วงรุ่งเรืองสูงสุดในปี 1942
-
แผนที่ของจักรวรรดิโปรตุเกส
-
ดินแดนภายใต้ราชวงศ์ชิง
-
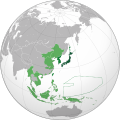
จักรวรรดิญี่ปุ่น ช่วงรุ่งเรืองสูงสุด
-
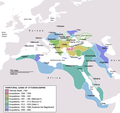
จักรวรรดิออตโตมันในปี 1683
เศรษฐกิจในจักรวรรดิ[แก้]
จีดีพีในรายการต่อไปนี้ ประมาณการจากจักรวรรดิในยุคปัจจุบันตั้งแต่คริสต์ศตวรรษที่ 18 ถึงคริสต์ศตวรรษที่ 20 ทั้งหมดเทียบจำนวนเงินดอลลาร์สหรัฐในปี 1990
ขนาดของจีดีพี[แก้]
 จักรวรรดิบริติช – $918.7 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (in 1938)[31]
จักรวรรดิบริติช – $918.7 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (in 1938)[31] ไรช์เยอรมัน – $375.6 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (in 1938)[31]
ไรช์เยอรมัน – $375.6 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (in 1938)[31] ญี่ปุ่น – $260.7 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (in 1938)[31]
ญี่ปุ่น – $260.7 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (in 1938)[31] รัสเซีย – $257.7 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (in 1917)[32]
รัสเซีย – $257.7 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (in 1917)[32] ราชวงศ์ชิง – $241.3 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (GDP decline to 1912, immediately before its downfall)[32]
ราชวงศ์ชิง – $241.3 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (GDP decline to 1912, immediately before its downfall)[32] จักรวรรดิอาณานิคมฝรั่งเศส – $234.1 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (in 1938)[31]
จักรวรรดิอาณานิคมฝรั่งเศส – $234.1 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (in 1938)[31] จักรวรรดิอิตาลี – $143.4 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (in 1938)[31]
จักรวรรดิอิตาลี – $143.4 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (in 1938)[31] ราชวงศ์อาฟชาริยะห์ – $119.85 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (in 1740)[32]
ราชวงศ์อาฟชาริยะห์ – $119.85 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (in 1740)[32] ออสเตรีย-ฮังการี – $100.5 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (in 1918)[33]
ออสเตรีย-ฮังการี – $100.5 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (in 1918)[33] จักรวรรดิโมกุล – $90.8 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (GDP decline in 1700)[32]
จักรวรรดิโมกุล – $90.8 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (GDP decline in 1700)[32] จักรวรรดิดัตช์ – $60 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (in 1900)
จักรวรรดิดัตช์ – $60 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (in 1900) จักรวรรดิออตโตมัน – $26.4 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (in 1923)[34]
จักรวรรดิออตโตมัน – $26.4 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (in 1923)[34] จักรวรรดิบราซิล – $13.6 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (in 1889)[33]
จักรวรรดิบราซิล – $13.6 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (in 1889)[33] จักรวรรดิโปรตุเกส – $12.6 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (in 1913)[33]
จักรวรรดิโปรตุเกส – $12.6 พันล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (in 1913)[33]
อ้างอิง[แก้]
- ↑ 1.000 1.001 1.002 1.003 1.004 1.005 1.006 1.007 1.008 1.009 1.010 1.011 1.012 1.013 1.014 1.015 1.016 1.017 1.018 1.019 1.020 1.021 1.022 1.023 1.024 1.025 1.026 1.027 1.028 1.029 1.030 1.031 1.032 1.033 1.034 1.035 1.036 1.037 1.038 1.039 1.040 1.041 1.042 1.043 1.044 1.045 1.046 1.047 1.048 1.049 1.050 1.051 1.052 1.053 1.054 1.055 1.056 1.057 1.058 1.059 1.060 1.061 1.062 1.063 1.064 1.065 1.066 1.067 1.068 1.069 1.070 1.071 1.072 1.073 1.074 1.075 1.076 1.077 1.078 1.079 1.080 1.081 1.082 1.083 1.084 1.085 1.086 1.087 1.088 1.089 1.090 1.091 1.092 1.093 1.094 1.095 1.096 1.097 1.098 1.099 1.100 1.101 1.102 1.103 1.104 1.105 1.106 1.107 1.108 1.109 1.110 1.111 1.112 1.113 1.114 1.115 1.116 1.117 1.118 1.119 1.120 1.121 Taagepera, Rein (September 1997). "Expansion and Contraction Patterns of Large Polities: Context for Russia" (PDF). International Studies Quarterly. 41 (3): 492–502. doi:10.1111/0020-8833.00053. JSTOR 2600793. เก็บ (PDF)จากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 2020-07-07. สืบค้นเมื่อ 2020-07-07.
- ↑ 2.000 2.001 2.002 2.003 2.004 2.005 2.006 2.007 2.008 2.009 2.010 2.011 2.012 2.013 2.014 2.015 2.016 2.017 2.018 2.019 2.020 2.021 2.022 2.023 2.024 2.025 2.026 2.027 2.028 2.029 2.030 2.031 2.032 2.033 2.034 2.035 2.036 2.037 2.038 2.039 2.040 2.041 2.042 2.043 2.044 2.045 2.046 2.047 2.048 2.049 2.050 2.051 2.052 2.053 2.054 2.055 2.056 2.057 2.058 2.059 2.060 2.061 2.062 2.063 2.064 2.065 2.066 2.067 2.068 2.069 2.070 2.071 2.072 2.073 2.074 2.075 2.076 2.077 2.078 2.079 2.080 2.081 2.082 2.083 2.084 2.085 2.086 2.087 2.088 2.089 2.090 2.091 2.092 2.093 2.094 2.095 2.096 2.097 2.098 2.099 2.100 2.101 2.102 2.103 2.104 2.105 2.106 2.107 2.108 2.109 2.110 2.111 2.112 2.113 2.114 2.115 2.116 2.117 2.118 2.119 Turchin, Peter; Adams, Jonathan M.; Hall, Thomas D. (December 2006). "East-West Orientation of Historical Empires" (PDF). Journal of World-Systems Research. 12 (2): 222–223. ISSN 1076-156X. เก็บ (PDF)จากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 2020-07-07. สืบค้นเมื่อ 2020-07-07.
- ↑ 3.000 3.001 3.002 3.003 3.004 3.005 3.006 3.007 3.008 3.009 3.010 3.011 3.012 3.013 3.014 3.015 3.016 3.017 3.018 3.019 3.020 3.021 3.022 3.023 3.024 3.025 3.026 3.027 3.028 3.029 3.030 3.031 3.032 3.033 3.034 3.035 3.036 3.037 3.038 3.039 3.040 3.041 3.042 3.043 3.044 3.045 3.046 3.047 3.048 3.049 3.050 3.051 3.052 3.053 3.054 3.055 3.056 3.057 3.058 3.059 3.060 3.061 3.062 3.063 3.064 3.065 3.066 3.067 3.068 3.069 3.070 3.071 3.072 3.073 3.074 3.075 3.076 3.077 3.078 3.079 3.080 3.081 3.082 3.083 3.084 3.085 3.086 3.087 3.088 3.089 3.090 3.091 3.092 3.093 3.094 3.095 3.096 3.097 3.098 3.099 3.100 3.101 3.102 3.103 3.104 3.105 3.106 3.107 3.108 Taagepera, Rein (1979). "Size and Duration of Empires: Growth-Decline Curves, 600 B.C. to 600 A.D.". Social Science History. 3 (3/4): 121–122, 124–129, 132–133. doi:10.2307/1170959. JSTOR 1170959.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Área Territorial Brasileira". www.ibge.gov.br (ภาษาโปรตุเกส). Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics. เก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 23 October 2016. สืบค้นเมื่อ 16 October 2016.
A primeira estimativa oficial para a extensão superficial do território brasileiro data de 1889. O valor de 8.337.218 km2 foi obtido a partir de medições e cálculos efetuados sobre as folhas básicas da Carta do Império do Brasil, publicada em 1883. [The first official estimate of the surface area of the Brazilian territory dates from 1889. A value of 8,337,218 km2 was obtained from measurements and calculations made on drafts of the Map of the Empire of Brazil, published in 1883.]
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Conrad, Sebastian (2014). "The Dialectics of Remembrance: Memories of Empire in Cold War Japan" (PDF). Comparative Studies in Society and History. 56 (1): 8. doi:10.1017/S0010417513000601. ISSN 0010-4175. JSTOR 43908281. S2CID 146284542. เก็บ (PDF)จากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 2020-07-08. สืบค้นเมื่อ 2020-07-07.
In 1942, at the moment of its greatest extension, the empire encompassed territories spanning over 7,400,000 square kilometers.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 James, David H. (2010-11-01). The Rise and Fall of the Japanese Empire (ภาษาอังกฤษ). Routledge. ISBN 9781136925467. เก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 6 July 2019. สืบค้นเมื่อ 11 September 2018.
by 1942, this 'Empire' covered about 3,285,000 square miles
- ↑ 7.00 7.01 7.02 7.03 7.04 7.05 7.06 7.07 7.08 7.09 Bang, Peter Fibiger; Bayly, C. A.; Scheidel, Walter (2020-12-02). The Oxford World History of Empire: Volume One: The Imperial Experience (ภาษาอังกฤษ). Oxford University Press. pp. 92–94. ISBN 978-0-19-977311-4.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Rodríguez, Jaime; Vincent, Kathryn (1997). "The Colonization and Loss of Texas: A Mexican Perspective". Myths, Misdeeds and Misunderstandings: The Roots of Conflict in US-Mexican Relations (First ed.). Wilmington, DE, USA: Scholarly Resources Inc. p. 47. ISBN 0-8420-2662-2. เก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 2020-06-15. สืบค้นเมื่อ 14 May 2020.
When it was founded in 1821, the Mexican Empire extended over 4,429,000 km2 (not including the 445,683 km2 temporarily added by the short-lived union of the Central American provinces).
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 Soldaten-Atlas (Tornisterschrift des Oberkommandos der Wehrmacht, Heft 39). Leipzig: Bibliographisches Institut. 1941. pp. 8, 32.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1
 Chisholm, Hugh, บ.ก. (1911). . สารานุกรมบริตานิกา ค.ศ. 1911. Vol. 11 (11 ed.). สำนักพิมพ์มหาวิทยาลัยเคมบริดจ์. pp. 804–828.
Chisholm, Hugh, บ.ก. (1911). . สารานุกรมบริตานิกา ค.ศ. 1911. Vol. 11 (11 ed.). สำนักพิมพ์มหาวิทยาลัยเคมบริดจ์. pp. 804–828.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Korchmina, Elena; Sharp, Paul (June 2020). "Denmark and Russia: What can we learn from the historical comparison of two great Arctic agricultural empires?" (PDF). European Historical Economics Society. p. 3. เก็บ (PDF)จากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 2020-07-08. สืบค้นเมื่อ 2020-07-04.
Around 1700, the Danish Empire covered around 3 million square kilometers
- ↑ Waters, Matthew (2005). Lanfranchi, Giovanni B.; Roaf, Michael; Rollinger, Robert (บ.ก.). "Media and Its Discontents". Journal of the American Oriental Society. 125 (4): 517–533. ISSN 0003-0279. JSTOR 20064424.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Townsend, Mary Evelyn; Peake, Cyrus Henderson (1941). European Colonial Expansion Since 1871 (ภาษาอังกฤษ). J.B. Lippincott. p. 19. เก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 2020-07-19. สืบค้นเมื่อ 2020-07-19.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 Turchin, Peter (2009). "A theory for formation of large empires" (PDF). Journal of Global History (ภาษาอังกฤษ). 4 (2): 202. doi:10.1017/S174002280900312X. ISSN 1740-0228. S2CID 73597670. คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิม (PDF)เมื่อ 2020-01-31. สืบค้นเมื่อ 2020-01-31.
- ↑ 15.00 15.01 15.02 15.03 15.04 15.05 15.06 15.07 15.08 15.09 15.10 15.11 15.12 15.13 15.14 15.15 15.16 15.17 15.18 15.19 15.20 15.21 15.22 15.23 15.24 15.25 15.26 15.27 15.28 15.29 15.30 15.31 15.32 15.33 15.34 15.35 15.36 15.37 15.38 15.39 15.40 15.41 15.42 15.43 15.44 15.45 15.46 15.47 15.48 15.49 15.50 15.51 15.52 15.53 Taagepera, Rein (1978). "Size and Duration of Empires: Growth-Decline Curves, 3000 to 600 B.C." (PDF). Social Science Research. 7 (2): 182–189. doi:10.1016/0049-089x(78)90010-8. ISSN 0049-089X. เก็บ (PDF)จากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 2020-07-07. สืบค้นเมื่อ 2020-07-07.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Hughes, William (1873). A Class-book of Modern Geography: With Examination Questions (ภาษาอังกฤษ). G. Philip & Son. p. 175. เก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 2020-08-26. สืบค้นเมื่อ 2020-08-26.
In size it is about 500,000 square miles
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Sundberg, Ulf (2018). Swedish defensive fortress warfare in the Great Northern War 1702-1710 (PDF). Åbo: Åbo Akademis förlag. p. 26. ISBN 978-951-765-897-3. OCLC 1113941754. คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิม (PDF)เมื่อ 2020-07-03.
In 1700, the Swedish Empire covered a land area of 990,000 square kilometers and had 2,500,000 inhabitants.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Cornell, James (1978). Lost Lands and Forgotten People (ภาษาอังกฤษ). Sterling Publishing Company. p. 24. ISBN 978-0-8069-3926-1.
Zimbabwe continued to grow, reaching the height of its power in 1700, under the rule of the Rozwi people. When the first Europeans arrived on the African coast, they heard tales of a great stone city, the capital of a vast empire. The tales were true, for the Rozwi controlled 240,000 square miles (624,000 sq km)
- ↑ 19.0 19.1
 Chisholm, Hugh, บ.ก. (1911). . สารานุกรมบริตานิกา ค.ศ. 1911. Vol. 03 (11 ed.). สำนักพิมพ์มหาวิทยาลัยเคมบริดจ์. pp. 2–39.
Chisholm, Hugh, บ.ก. (1911). . สารานุกรมบริตานิกา ค.ศ. 1911. Vol. 03 (11 ed.). สำนักพิมพ์มหาวิทยาลัยเคมบริดจ์. pp. 2–39.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 20.3 20.4 20.5 Taagepera, Rein (1978). "Size and duration of empires: Systematics of size" (PDF). Social Science Research (ภาษาอังกฤษ). 7 (2): 116–117. doi:10.1016/0049-089X(78)90007-8. ISSN 0049-089X. เก็บ (PDF)จากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 2020-07-07. สืบค้นเมื่อ 2020-07-07.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Singh, Amarpal (2010-08-15). The First Anglo-Sikh War (ภาษาอังกฤษ). Amberley Publishing Limited. ISBN 978-1-4456-2038-1.
By 1839, the year of his death, the Sikh kingdom extended from Tibet and Kashmir to Sind and from the Khyber Pass to the Himalayas in the east. It spanned 600 miles from east to west and 350 miles from north to south, comprising an area of just over 200,000 square miles.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Rashev, Rasho (2008). Българската езическа култура VII -IX в./Bulgarian Pagan Culture VII – IX cтр. 38 (ภาษาบัลแกเรีย). Класика и стил. ISBN 9789543270392.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Wesseling, H. L. (2015-10-23). The European Colonial Empires: 1815-1919 (ภาษาอังกฤษ). Routledge. p. 93. ISBN 978-1-317-89507-7. เก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 2020-07-08. สืบค้นเมื่อ 2020-07-03.
Islam spread quickly in Hausaland, which, after the jihad of 1804, was incorporated into the Sokoto Caliphate, a vast empire of 400,000 square kilometres.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 Iliffe, John (1995-08-25). Africans: The History of a Continent (ภาษาอังกฤษ). Cambridge University Press. p. 143. ISBN 978-0-521-48422-0.
At its peak around 1820 the empire embraced over 250,000 square kilometres [...]
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 Gluckman, Max (1960). "The Rise of a Zulu Empire". Scientific American. 202 (4): 162. Bibcode:1960SciAm.202d.157G. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0460-157. ISSN 0036-8733. JSTOR 24940454. สืบค้นเมื่อ 2020-07-07.
By 1822 he had made himself master over 80,000 square miles
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 Thornton, John (1998-04-28). Africa and Africans in the Making of the Atlantic World, 1400-1800 (ภาษาอังกฤษ). Cambridge University Press. p. 104. ISBN 978-0-521-62724-5.
By 1680, the Oyo Empire (in Nigeria) may have exceeded 150,000 square kilometers, though not by much.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 Hughes, William; Williams, J. Francon (1892). A Class-book of Modern Geography: With Examination Questions, Notes, & Index (ภาษาอังกฤษ). G. Philip & son. p. 281. เก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 2021-05-30.
It has an area of perhaps 50,000 square miles.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 Blanford, Adam Jared (2014). "Rethinking Tarascan Political and Spatial Organization" (PDF). Anthropology Graduate Theses & Dissertations. University of Colorado Boulder: 6. S2CID 147339315. คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิม (PDF)เมื่อ 2020-02-13. สืบค้นเมื่อ 2020-07-03.
By A.D. 1450, the Tarascan Uacúsecha were leaders of an empire that spanned 75,000 square kilometers of west Mexico
- ↑ "NĀDER SHAH – Encyclopaedia Iranica".
- ↑ Soucek, Svat (2000). A History of Inner Asia. Cambridge University Press. p. 179. ISBN 9780521657044.
In 1740 Nadir Shah, the new ruler of Iran, crossed the Amu Darya and, accepting the submission of Muhammad Hakim Bi which was then formalized by the acquiescence of Abulfayz Khan himself, proceeded to attack Khiva. When rebellions broke out in 1743 upon the death of Muhammad Hakim, the shah dispatched the ataliq’s son Muhammad Rahim Bi, who had accompanied him to Iran, to quell them.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 31.2 31.3 31.4 Harrison (1998, pp. 3,7).
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 32.2 32.3 Maddison, op cit. For alternate estimates, see the Economic History Services' USA/UK GDP search tool. เก็บถาวร 2012-01-18 ที่ เวย์แบ็กแมชชีน
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 33.2 Broadberry and Harrison (2005).
- ↑ Pamuk (2005[ต้องการเลขหน้า]).





















![จักรวรรดิเปอร์เซีย ในยุคชาห์นาเดอร์[29][30]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/f3/AfsharidEmpireIran.png/120px-AfsharidEmpireIran.png)
