ผู้ใช้:Robosorne/กระบะทราย 3

มาร์ค ทิลเดนMark W Tilden เป็นนักวิทยาการหุ่นยนต์ และเป็นที่รู้จักกันดีในฐานะของผู้บุกเบิกแนวคิดทางในการประดิษฐ์หุ่นยนต์ที่มีการเคลื่อนที่ซับซ้อนแต่ใช้การออกแบบวงจรทางไฟฟ้าที่เรียบง่าย โดยหุ่นยนต์ของทิวเดนส่วนใหญ่มักจะใช้วงจรแอนะล็อกอย่างง่าย (อย่างเช่น อุปกรณ์เปรียบเทียบ (Comparator) และ ออสซิลเลเตอร์ (Oscillator) )ในการสร้างสัญญาณสั่งให้ตัวขับ (actuator) ทำงานได้ และไม่ได้อาศัยไมโครคอนโทรลเลอร์ในการควบคุมและประมวลผลสัญญาณ ซึ่งต่อมาแนวคิดดังกล่าวได้รับการต่อยอดเป็นแนวคิดที่เรียกว่า หุ่นยนต์แบบ BEAM นอกจากนี้ ทิลเดนยังเป็นที่รู้จักกันดีในฐานะผู้ประดิษฐ์หุ่นยนต์ฮิวแมนนอยด์ที่มีชื่อว่า โรโบซาเปี้ยน (Robosapien) ผลิตโดย บริษัทWowWee
ประวัติ[แก้]
ทิวเดน เกิดที่สหราชอาณาจักร ในปี ค.ศ. 1961 แต่เติบโตในแคนาดา และเข้าศึกษาระดับอุดมศึกษาที่มหาวิทยาลัยวอเตอร์ลู (University of Waterloo) ต่อมาเข้าทำงานที่ห้องทดลอง แห่งชาติ ลอส อลามอส (Los Alamos National Laboratory) ซึ่งระหว่างนี้ ทิวเดน ได้ประดิษฐ์หุ่นยนต์อย่าง SATbot ซึ่งมีความสามารถในการจัดเรียงตัวเองได้ตามแนวสนามแม่เหล็กของโลก นอกจากนี้ยังพัฒนาทฤษฎีและการประยุกต์โครงข่ายประสาท ยานสำรวจระหว่างดาวเคราะห์ การศึกษาพฤติกรรมบนหุ่นยนต์แบบ BEAMที่ใช้แผงเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ ปัจจุบัน ทิวเดน ทำงานเป็นนักออกแบบหุ่นยนต์อิสระในฮ่องกง ที่ปรึกษา และผู้บรรยาย
ผลงาน[แก้]
ในบรรดาผลงานที่เป็นสินค้าของบริษัทWowWee ผลงานที่เป็นที่รู้จักได้แก่ หุ่นยนต์ชีวรูป (biomorphic robot) ได้แก่ B.I.O. Bugs (2001), Constructobots (2002), G.I Joe Hoverstrike (2003), โรโบซาเปี้ยน RoboSapien (2004), โรโบซาเปี้ยน วี 2 Robosapien v2 (2005), โรโบแรปเตอร์ Roboraptor (2005), โรโบเพ็ต Robopet (2005), โรโบแรปไทน์ Roboreptile (2006), RS Media (2006,พัตนาร่วมกับ ดาวิน ซูเฟอร์ (Davin Sufer) และ แมกซ์เวล โบรก์ (Maxwell Bogue) ), โรโบควอด Roboquad (2007), โรโบโบอา Roboboa (2007), เฟอร์มิซาเปี้ยน Femisapien (2008), โจบ๊อต (Joebot) (2009),และ รูมสคูพเพอร์ (Roomscooper) (2010) [1] ทิวเดน ยังเคยปรากฏตัวสือโทรทัศน์ อย่างเช่น สารคดี "Robots Rising" (ช่อง Discovery), "The Shape of Life" (ช่อง PBS), "TechnoSpy" (ช่อง TLC), "Extreme Machines - Incredible Robots" (ช่อง TLC), "The Science behind Star Wars" (ช่อง Discovery) และในสือสิ่งพิมพ์ และสือออนไลน์ และยังเคยเป็นที่ปรึกษาทางด้านเทคนิคให้แก่หนังเรื่อง Lara Croft: Tomb Raider ในปี ค.ศ. 2001 นอกจากนี้หุ่นยนต์ของทิวเดน ยังปรากฏในหนังและละครโทรทัศนหลายเรื่อง อาทิ เช่น The 40 Year Old VirginPaul Blart Mall CopX-Men: The Last Stand และเป็นอุปกรณ์ประกอบฉากประจำซีรีย์The Big Bang Theory
เพิ่มเติม[แก้]
แหล่งข้อมูลอื่น[แก้]
- EvoSapien - A website dedicated on Hacking the Robosapien Robot, lots of mods, and useful information, schematics, codings, pictures, videos, including the new line of Mark Tilden Robots.
- EvoRaptor A Website dedicated to the Roboraptor, pictures, videos, internals, videos, hacks, and lots more. Created 2005 by M.W Tilden and Wow Wee and hacked by fans and the Maker community.
- RoboCommunity - The official WowWee Robotics user community detailing hacks, mods, and how-it-was-made pictorial articles on Mark's robots.
- Superstreng Podcast- A September 2006 podcast interview with Mark Tilden, conducted by Eirik Newth for Norwegian science radio show Superstreng.
- Robotsrule - Detailed information site on many commercially available entertainment robots.
- Solarbotics - On-line store for parts, plans, kits, and history of BEAM robotics.
- BEAM Discussion Group - Active on-line discussion group of BEAM robots, builders, events, and history.
- "Robot" Magazine - Detailed article on Mark Tilden's history, philosophy, and robotics approach, with images.
อ้างอิง[แก้]
| [[วิกิพีเดีย:|ข้อมูลบุคคล]] | |
|---|---|
| ชื่อ | Tilden, Mark} |
| ชื่ออื่น | "BotGod" |
| รายละเอียดโดยย่อ | Large enough to influence tides. |
| วันเกิด | 1961 |
| สถานที่เกิด | Stroud, England |
| วันตาย | |
| สถานที่ตาย | |
แม่แบบ:BEAM robotics แม่แบบ:WowWee Robots
ฟังก์ชันเลียปูนอฟ (อังกฤษ: Lyapunov functions) เป็นฟังก์ชันที่ใช้ในการการหาเสถียรภาพของระบบพลวัตในทฤษฎีเสถียรภาพของเลียปูนอฟ โดยตั้งตามชื่อของ อเล็กซานเดอร์ มิคาอิลโลวิช เลียปูนอฟ นักคณิตศาสตร์ชาวรัสเซีย (6 มิถุนายน ค.ศ. 1857 – 3 พฤศจิกายน ค.ศ. 1918) ฟังก์ชันนี้มีบทบาทสำคัญมากในทฤษฎีเสถียรภาพ และ ทฤษฎีระบบควบคุม
ในขณะนี้ยังไม่มีวิธีการทั่วไปในการหาฟังก์ชันเลียปูนอฟของระบบในกรณีทั่วไป เพราะในทฤษฎีเสถียรภาพของเลียปูนอฟสามารถบอกได้เพียงว่า ถ้าหากฟังก์ชันเลียปูนอฟสอดคล้องกับเกณฑ์ของเสถียรภาพจึงสามารถสรุปได้ว่าระบบนั้นมีเสถียรภาพ แต่ในทางกลับกัน ระบบที่มีเสถียรภาพไม่สามารถบ่งบอกได้ว่าฟังก์ชันแบบใดที่เป็นฟังก์ชันเลียปูนอฟได้ ดังนั้นในการพิสูจน์เสถียรภาพของระบบ จะกระทำโดยการสร้างฟังก์ชันที่มีคุณสมบัติตรงตามคุณสมบัติฟังก์ชันที่เข้าเกณฑ์การเป็นฟังก์เลียปูนอฟจะเรียกว่า ฟังก์ชันพลังงาน[1] (Energy function หรือ Lyapunov-candidate-functions) กล่าวคือ การที่ไม่สามารถหาฟังก์ชันเลียปูนอฟได้นันไม่ได้เป็นการพิสูจน์ได้ว่าระบบนั้นไม่ได้มีเสถียรภาพ แต่การที่สามารถหาฟังก์ชันเลียปูนอฟมาพิสูจน์เสถียรภาพได้เป็นการพิสูจน์ได้ว่าระบบนั้นๆมีเสถียรภาพ
ในทางปฎิบัติสำหรับระบบพลวัตทางฟิสิกส์ มักนิยมใช้กฎอนุรักษ์ต่างๆในการสร้างฟังก์ชันพลังงานได้
นิยามของฟังก์ชันพลังงาน[แก้]
- กำหนดให้ เป็นฟังก์ชันต่อเนื่องและเป็นสเกลาร์
- จะเป็นฟังก์ชันพลังงานถ้าหาก เป็นฟังก์ชันบวกแน่นอนเฉพาะแห่ง (locally positive-definite function) กล่าวคือ
- โดยที่ เป็นเซตบริเวณใกล้เคียงรอบจุด
- หมายเหตุ: ตัวอย่างของฟังก์ชันพลังงาน ได้แก่ [1] โดยที่ กล่าวคือ คือเมทริกซ์บวกแน่นอน
นิยามของจุดสมดุลของระบบ[แก้]
- กำหนดให้
- เป็นระบบพลวัตอัตตาณัติที่กำหนดให้ โดยมีจุดสมดุลกำหนดให้เป็น ดังนั้น
โดยไม่เสียความเป็นนัยยะทั่วไป เราสามารถแปลงพิกัดในอยู่ในรูป เพื่อให้ระบบที่เราจะพิจารณาต่อไปมีจุดสมดุลอยู่ที่จุดกำเนิด ทำให้ความสะดวกต่อการพิจารณาต่อไป ดังต่อไปนี้
พื้นฐานของทฤษฎีเลียปูนอฟสำหรับระบบอัตตาณัติ[แก้]
- กำหนดให้ เป็นจุดสมดุลของระบบอัตตาณัติ
- และให้
เป็นเป็นอนุพันธ์เชิงเวลาของฟังก์ชันพลังงาน
เสถียรภาพของจุดสมดุล[แก้]
ถ้าฟังก์ชันพลังงาน เป็นบวกแน่นอนเฉพาะที่ และอนุพันธ์เชิงเวลาของฟังก์ชันพลังงานเป็นลบกึ่งแน่นอนเฉพาะที่ (locally negative semidefinite):
สำหรับย่าน รอบจุด จะสรุปได้ว่าจุดสมดุลนั้นมีเสถียรภาพ (stable)
เสถียรภาพเฉพาะที่เชิงเส้นกำกับ[แก้]
ถ้าฟังก์ชันพลังงาน เป็นบวกแน่นอนเฉพาะที่ และอนุพันธ์เชิงเวลาของฟังก์ชันพลังงานเป็นลบแน่นอนเฉพาะที่ (locally negative definite):
สำหรับย่าน รอบจุด จะสรุปได้ว่าจุดสมดุล มีเสถียรภาพเฉพาะที่เชิงเส้นกำกับ (locally asymptotically stable)
เสถียรภาพวงกว้างเชิงเส้นกำกับ[แก้]
ถ้าฟังก์ชันพลังงาน เป็นบวกแน่นอนวงกว้าง (globally positive definite) และอนุพันธ์เชิงเวลาของฟังก์ชันพลังงานเป็นลบแน่นอนวงกว้าง (globally negative definite):
จะสรุปได้ว่าจุดสมดุล มีเสถียรภาพวงกว้างเชิงเส้นกำกับ (globally asymptotically stable)
- หมายเหตุ :ฟังก์ชันพลังงาน จะไม่มีขอบเขตถ้า
ตัวอย่าง[แก้]
พิจารณาสมการอนุพันธ์ ที่มีคำตอบเป็น โดยที่ :
จะเห็นว่า มีค่าเป็นบวกรอบจุดกำเนิด ซึ่งเราสามารถนำมาเป็นฟังก์ชันพลังงานได้ กำหนดให้ โดยที่ ดังนั้น
จะเห็นได้ว่าระบบที่ถูกอธิบายด้วยสมการอนุพันธ์ข้างต้นมีเสถียรภาพเชิงเส้นกำกับรอบจุดกำเนิด
เพิ่มเติม[แก้]
อ้างอิง[แก้]
- เอริก ดับเบิลยู. ไวส์สไตน์, "Lyapunov Function" จากแมทเวิลด์.
- Khalil, H.K. (1996). Nonlinear systems. Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River, NJ.
แหล่งข้อมูลอื่น[แก้]
- Example of determining the stability of the equilibrium solution of a system of ODEs with a Lyapunov function
- Some Lyapunov diagrams

จอห์น รากัซซินี (John Ralph Ragazzini 1912 – November 22, 1988) เป็นวิศวกรไฟฟ้าชาวอเมริกัน และศาสตราจารย์ทางด้านวิศวกรรมไฟฟ้า รากัซซินี เกิดที่รัฐนิวยอร์กสำเร็จการศึกษาระดับปริญญาบัณฑิตทางด้านวิทยาศาสตร์และวิศวกรรมไฟฟ้าจากวิทยาลัยประจำเมืองนิวยอร์ก (City College of New York) ในปี ค.ศ. 1932 และ ปี ค.ศ. 1933 ตามลำดับ และเข้ารับการศึกษาทางด้านอักษรศาสตร์มหาบัณฑิต (A.M.) และระดับปริญญาเอกด้านวิศวกรรมไฟฟ้าที่ Columbia University ในปี ค.ศ. 1939 และ ค.ศ. 1941
นอกจากนี้ รากัซซินี ยังเคยเป็นคณบดีประจำคณะวิศวกรรมและวิทยาศาสตร์แห่งมหาวิทยาลัยนิวยอร์ก (New York University)และในระหว่างสงครามโลกครั้งที่สอง รากัซซินียังเคยมีส่วนร่วมในโครงการแมนฮัดตัน (Manhattan Project) ขณะดำรงตำแหน่งเป็นหัวหน้าภาควิชาวิศวกรรมไฟฟ้าที่มหาวิทยาลัยโคลัมเบีย
รากัซซินี มีลูกศิษย์ที่มีชื่อเสียงสาขาทฤษฎีระบบควบคุมในเวลาต่อมาหลายคน ได้แก่ รูดอฟ คาลมาน (Rudolf Kalman) ผู้คิดค้นตัวกรองคานมาน(Kalman filter) และเป็นผู้นำเสนอปริภูมิสถานะมาใช้ในการสร้างแบบจำลองทางคณิตศาสตร์ของระบบ อันเป็นการนำองค์ความรู้ของทฤษฎีระบบควบคุมไปสู่ยุดใหม่ ที่เรียกว่า ทฤษฎีระบบควบคุมสมัยใหม่ () และ อีไลเอฮู อิมบราแฮม จัวรี่ (Eliahu Ibraham Jury) ผู้มีส่วนร่วมในการพัฒนาการแปลง Z (Z-transform) และคิดค้นการแปลง Z ขั้นสูง และ ล็อทฟี่ แอสเกอร์ ซาเด็ท (Lotfi Asker Zadeh) ผู้คิดค้นเซตวิภัชนัยFuzzy sets และ ตรรกศาสตร์คลุมเครือ Fuzzy logic
ในปี ค.ศ. 1952 รากัซซินี และ ซาเด็ท ได้ร่วมกันพัฒนา การแปลง Z สำหรับการประมวลและการวิเคาระห์สัญญาณบนโดนเมนเวลาวิยุต (discrete-time signal processing)
[1]
ในปี ค.ศ. 1979 สภาวิชาการการควบคุมอัตโนมัติแห่งสหรัฐอเมริกา (American Automatic Control Council) ได้ตั้งรางวัล จอห์น อาร์ รากัซซินี (John R. Ragazzini Award) เพื่อเป็นรางวัลที่มอบให้แก่นักวิจัยที่มีคุณูปการแก่วงการวิชาการทฤษฎีระบบ และ รากัซซินี เป็นผู้ที่ได้รับรางวัลนี้คนแรก
References[แก้]
External links[แก้]
- John R. Ragazzini's Obituary in New York Times
- John R. Ragazzini's on the Mathematics Genealogy Project's page.
| [[วิกิพีเดีย:|ข้อมูลบุคคล]] | |
|---|---|
| ชื่อ | Ragazzini, John} |
| ชื่ออื่น | |
| รายละเอียดโดยย่อ | |
| วันเกิด | 1912 |
| สถานที่เกิด | |
| วันตาย | November 22, 1988 |
| สถานที่ตาย | |
คำเตือน: หลักเรียงลำดับปริยาย "Ragazzini, John" ได้ลบล้างหลักเรียงลำดับปริยาย "Tilden, Mark" ที่มีอยู่ก่อนหน้า
คำเตือน: หลักเรียงลำดับปริยาย "Systems engineering" ได้ลบล้างหลักเรียงลำดับปริยาย "Ragazzini, John" ที่มีอยู่ก่อนหน้า
รูดอล์ฟ อีมิว คาลมาน Rudolf Emil Kálmán | |
|---|---|
| เกิด | 19 พฤษภาคม ค.ศ. 1930 บูดาเปสต์, ราชอาณาจักรฮังการี (Kingdom of Hungary) |
| สัญชาติ | ชาวฮังการี-โดยกำเนิด สหรัฐอเมริกา |
| ศิษย์เก่า | สถาบันเทคโนโลยีแมสซาชูเซตส์; มหาวิทยาลัยโคลัมเบีย |
| รางวัล | IEEE Medal of Honor; National Medal of Science; Charles Stark Draper Prize ; รางวัลเกียวโต ปี ค.ศ. 1985 (Kyoto Prize) [1] |
| อาชีพทางวิทยาศาสตร์ | |
| สาขา | วิศวกรรมไฟฟ้า; คณิตศาสตร์; ทฤษฎีระบบควบคุม |
| สถาบันที่ทำงาน | มหาวิทยาลัยสแตนฟอร์ด; มหาวิทยาลัยฟลอริดา; สถาบันเทคโนโลยีสวิส ซูริค |
| อาจารย์ที่ปรึกษาในระดับปริญญาเอก | จอห์น รากัซซินี |
รูดอล์ฟ (รูดี้) อีมิว คาลมาน (ฮังการี: Rudolf (Rudy) Emil Kálmán 19 พฤษภาคม พ.ศ. 1930 - ปัจจุบัน) [2] เป็นวิศวกรไฟฟ้า นักทฤษฎีระบบเชิงคณิศาสตร์ และผู้พัฒนาตัวกรองคานมาน (Kalman filter) และเป็นผู้นำเสนอแบบจำลองปริภูมิสถานะ และนำเสนอแนวคิดเรื่องสภาพควบคุมได้และสภาพสังเกตได้ มาใช้ในการสร้างแบบจำลองทางคณิตศาสตร์ของระบบ อันเป็นการนำองค์ความรู้ของทฤษฎีระบบควบคุมไปสู่ยุคใหม่ ที่เรียกว่า ทฤษฎีระบบควบคุมสมัยใหม่ (modern control theory) และในวันที่ 7 ตุลาคม ค.ศ. 2009 คาลมาน ได้รับรางวัลเหรียญวิทยาศาสตร์แห่งชาติ (National Medal of Science) จากประธานาธิบดีบารัก โอบามา สำหรับผลงานทางด้านทฤษฎีระบบควบคุม
ชีวประวัติ[แก้]
รูดอล์ฟ คาลมาน เกิดที่เมืองบูดาเปสต์ ประเทศฮังการี และอพยพมาสหรัฐอเมริกาในปี ค.ศ. 1943 และสำเร็จการศึกษาระดับปริญญาตรีและโททางด้านวิศวกรรมไฟฟ้าจากสถาบันเทคโนโลยีแมสซาชูเซตส์ในปี ค.ศ. 1953 และ ค.ศ. 1954 ตามลำดับ และปริญญาเอกที่มหาวิทยาลัยโคลัมเบีย ในปี ค.ศ. 1957
คาลมาน เริ่มงานเป็นนักคณิตศาสตร์ ที่สถาบันวิจัยสำหรับการศึกษาขั้นสูง (Research Institute for Advanced Studies)ในบอลทิมอร์ รัฐแมริแลนด์ ในปี ค.ศ. 1958 จนถึงปี ค.ศ. 1964 และเข้าดำรงตำแหน่งศาสตราจารย์ที่มหาวิทยาลัยสแตนฟอร์ดในปี ค.ศ. 1964 ถึงปี ค.ศ. 1971 และดำรงตำแหน่งศาสตราจารย์และผู้อำนวยการศูนย์ทฤษฎีระบบเชิงคณิตศาสตร์ (Center for Mathematical System Theory) ที่มหาวิทยาลัยฟลอริดาในปี ค.ศ. 1971 ถึงปี ค.ศ. 1992 ในปี ค.ศ. 1973 คาลมานยังเข้าดำรงตำแหน่งประธานของภาควิชา ทฤษฎีระบบเชิงคณิตศาสตร์ที่สถาบันเทคโนโลยีสวิส ซูริค (ETH Zurich) อีก ตำแหน่งด้วย
คาลมาน ยังเป็นสมาชิกของสมาคมวิทยาศาสตร์แห่งชาติของสหรัฐอเมริกา (U.S. National Academy of Sciences) และสมาคมวิศวกรรมศาสตร์แห่งชาติ (National Academy of Engineering) และสมาคมศิลปะและวิทยาศาสตร์แห่งสหรัฐอเมริกา (American Academy of Arts and Sciences) นอกจากนี้ คาลมานยังเป็นสมาชิกชาวต่างชาติของ สมาคมวิทยาศาสตร์แห่งชาติของฮังการี ฝรั่งเศส และรัสเซีย และยังได้รับปริญญาดุษฎีบัณฑิตกิตติมาศักดิ์มหาวิทยาลัยต่างๆเป็นจำนวนมาก
คาลมาน ได้รับเหรียญเกียรติยศของ IEEE (IEEE Medal of Honor) ในปี ค.ศ. 1974 และเหรียญ IEEE Centennial Medal ในปี ค.ศ. 1984 รางวัลเกียวโตจากกองทุนอินาโมริ (Kyoto Prize) ในสาขาเทคโนโลยีขั้นสูง ค.ศ. 1985 และ Steele Prize จากสมาคมคณิตศสตร์อเมริกัน (American Mathematical Society)ในปี ค.ศ. 1987 รางวัล Richard E. Bellman Control Heritage Awardในปี ค.ศ. 1997 และ Charles Stark Draper Prize จากสมาคมวิศวกรรมศาสตร์แห่งชาติใน ค.ศ. 2008 For this work, U.S. President Barack Obama awarded Kálmán with the National Medal of Science on October 7, 2009.
ผลงาน[แก้]
Kálmán is an วิศวกรไฟฟ้า by his undergraduate and graduate education at สถาบันเทคโนโลยีแมสซาชูเซตส์. and มหาวิทยาลัยโคลัมเบีย, and he is noted for his co-invention of the ตัวกรองคาลมาน หรือ ตัวกรองคาลมาน-บุทซี่ (Kalman-Bucy Filter), which is a mathematical technique widely used in the digital computers of ระบบควบคุมs, ระบบนำทาง (navigation systems), การบิน (avionics), and outer-space vehicles to extract a การประมวลผลสัญญาณ from a long sequence of noisy and/or incomplete technical measurements, usually those done by electronic and gyroscopic systems.
Kálmán's ideas on filtering were initially met with vast skepticism, so much so that he was forced to do the first publication of his results in วิศวกรรมเครื่องกล, rather than in electrical engineering or systems engineering. Kálmán had more success in presenting his ideas, however, while visiting สแตนลี่ เอฟ. ชมิคท์ Stanley F. Schmidt at the ศูนย์วิจัยแอมส์ ของนาซ่า (NASA Ames Research Center) in 1960. This led to the use of Kálmán filters during the โครงการอะพอลโล, and furthermore, in the NASA กระสวยอวกาศ, in Navy เรือดำน้ำs, and in unmanned อวกาศยาน vehicles and weapons, such as ขีปนาวุธนำวิถี (cruise missile)
อ้างอิง[แก้]
- ↑ รายชื่อผู้ได้รับรางวัลเกียวโต รายปี
- ↑ National Science Fundation – The President's National Medal of Science: Recipient Details: RUDOLF E. KÁLMÁN
- Kalman, R.E. (1960). "A new approach to linear filtering and prediction problems" (PDF). Journal of Basic Engineering. 82 (1): 35–45. สืบค้นเมื่อ 2008-05-03.
- Kalman, R.E. (1961). "New Results in Linear Filtering and Prediction Theory". สืบค้นเมื่อ 2008-05-03.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal ต้องการ|journal=(help); ไม่รู้จักพารามิเตอร์|coauthors=ถูกละเว้น แนะนำ (|author=) (help)
แหล่งข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม[แก้]
- The Kalman Filter website
- Kyoto Prize
- For Kálmán's PhD students see Rudolf Emil Kálmán on the Mathematics Genealogy Project page.
- Biography of Kalman from the IEEE
แม่แบบ:IEEE Medal of Honor Laureates 1951-1975 แม่แบบ:Richard E. Bellman Control Heritage Award 1979-2000 Laureates
| [[วิกิพีเดีย:|ข้อมูลบุคคล]] | |
|---|---|
| ชื่อ | Kalman, Rudolf Emil} |
| ชื่ออื่น | |
| รายละเอียดโดยย่อ | |
| วันเกิด | May 19, 1930 |
| สถานที่เกิด | Budapest, Hungary |
| วันตาย | |
| สถานที่ตาย | |
คำเตือน: หลักเรียงลำดับปริยาย "Kalman, Rudolf Emil" ได้ลบล้างหลักเรียงลำดับปริยาย "Systems engineering" ที่มีอยู่ก่อนหน้า In mathematics, the term positive-definite function may refer to a couple of different concepts.
In dynamical systems[แก้]
A real-valued, continuously differentiable function f is positive definite on a neighborhood of the origin, D, if and for every non-zero .[1][2]
A function is negative definite if the inequality is reversed. A function is semidefinite if the strong inequality is replaced with a weak ( or ) one.
In analysis[แก้]
A positive-definite function of a real variable x is a complex-valued function f:R → C such that for any real numbers x1, ..., xn the n×n matrix
is positive semi-definite (in particular, A should be Hermitian, therefore f(-x) is the complex conjugate of f(x)).
In particular, it is necessary (but not sufficient) that
(these inequalities follow from the condition for n=1,2.)
Bochner's theorem[แก้]
Positive-definiteness arises naturally in the theory of the Fourier transform; it is easy to see directly that to be positive-definite it is sufficient for f to be the Fourier transform of a function g on the real line with g(y) ≥ 0.
The converse result is Bochner's theorem, stating that any continuous positive-definite function on the real line is the Fourier transform of a (positive) measure.[3]
Applications[แก้]
In statistics, and especially Bayesian statistics, the theorem is usually applied to real functions. Typically, one takes n scalar measurements of some scalar value at points in and one requires that points that are closely separated have measurements that are highly correlated. In practice, one must be careful to ensure that the resulting covariance matrix (an n-by-n matrix) is always positive definite. One strategy is to define a correlation matrix A which is then multiplied by a scalar to give a covariance matrix: this must be positive definite. Bochner's theorem states that if the correlation between two points is dependent only upon the distance between them (via function f()), then function f() must be positive definite to ensure the covariance matrix A is positive definite. See Kriging.
In this context, one does not usually use Fourier terminology and instead one states that f(x) is the characteristic function of a symmetric PDF.
Generalisation[แก้]
One can define positive-definite functions on any locally compact abelian topological group; Bochner's theorem extends to this context. Positive-definite functions on groups occur naturally in the representation theory of groups on Hilbert spaces (i.e. the theory of unitary representations).
References[แก้]
- Christian Berg, Christensen, Paul Ressel. Harmonic Analysis on Semigroups, GTM, Springer Verlag.
- Z. Sasvári, Positive Definite and Definitizable Functions, Akademie Verlag, 1994
- Wells, J. H.; Williams, L. R. Embeddings and extensions in analysis. Ergebnisse der Mathematik und ihrer Grenzgebiete, Band 84. Springer-Verlag, New York-Heidelberg, 1975. vii+108 pp.
- ↑ Verhulst, Ferdinand (1996). Nonlinear Differential Equations and Dynamical Systems (2nd ed. ed.). Springer. ISBN 3-540-60934-2.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help) - ↑ Hahn, Wolfgang (1967). Stability of Motion. Springer.
- ↑ Bochner, Salomon (1959). Lectures on Fourier integrals. Princeton University Press.
โดยไม่สูญเสียนัยยะทั่วไป Without loss of generality abbreviated to WLOG; less commonly stated as without any loss of generality or with no loss of generality) เป็นศัพท์ที่ใช้กันในทางคณิตศาสตร์ ซึ่งมักใช้ในการพิสูจน์ โดย. The term is used before an assumption in a proof which narrows the premise to some special case; it is implied that the proof on this subset can be easily applied to all others (or that all other cases are trivial). Thus, given a proof of the special case, it is trivial to show that the conclusions follow from the full premise.
This often requires the presence of symmetry. For example, if two numbers are called x, y, and it is known that x < y, then any relationship proved based on this assumption will hold for the complementary relation, y < x, because the roles of x and y are interchanged, but the proof is symmetric in the two variables. In other words, if we know that P(x, y) is true if and only if P(y, x) is true, then without loss of generality it is enough to show P(x, y) is true (since P(y, x) then immediately follows, by symmetry). (In this context, we call P symmetric.)
Example[แก้]
Consider the following theorem (which is a case of the Pigeonhole Principle):
If three objects are each painted either red or blue, then there must be two objects of the same color.
A proof:
Assume without loss of generality that the first object is red. If either of the other two objects is red, we are finished; if not, the other two objects must both be blue and we are still finished.
See also[แก้]
External links[แก้]
- WLOG on PlanetMath
บทความนี้ยังต้องการเพิ่มแหล่งอ้างอิงเพื่อพิสูจน์ความถูกต้อง |
| Robosorne/กระบะทราย 3 | |
|---|---|
 สัญลักษณ์รายการ | |
| ประเภท | การวิพากษ์ปัญหาสังคม, ประวัติศาสตร์และวัฒนธรรม |
| ประเทศแหล่งกำเนิด | |
| ภาษาต้นฉบับ | ภาษาไทย |
| จำนวนตอน | 48 ตอน (นับถึงวันที่ 19 พฤศจิกายน 2554) |
| การผลิต | |
| ความยาวตอน | 30 นาที |
| ออกอากาศ | |
| เครือข่าย | วอยซ์ ทีวี |
| ออกอากาศ | 6 กุมภาพันธ์ พ.ศ. 2554 – ปัจจุบัน |
คิดเล่นเห็นต่างกับคำผกา เป็นรายการโทรทัศน์ออกอากาศทางวอยซ์ ทีวี เดิมออกอากาศเฉพาะวันอาทิตย์ ปัจจุบันออกอากาศทุกวันเสาร์และวันอาทิตย์ เวลา 21.30-22.00 น. โดยมีพิธีกรคือ คำ ผกา และ อรรถ บุนนาค เนื้อหาเป็นการหยิบยกปัญหาในสังคมมาวิเคราะห์เชิงลึก ทั้งในแง่มุมเชิงประวัติศาสตร์ สังคม วัฒนธรรม และมีการวิเคราะห์เชิงเปรียบเทียบระหว่างวัฒนธรรมไทยและต่างประเทศ ภายใต้แนวคิด "คิดเล่น-เห็นต่าง" ในช่วงท้ายของรายการจะมีการแนะนำหนังสือที่มีเนื้อหาเกี่ยวข้างกับประเด็นประจำสัปดาห์นั้น
เนื้อหารายการ[แก้]
เนื่องจากทางรายการมีการหยิบยกประเด็นในสังคมที่ยังเป็นข้อถกเถียงกันอยู่มาก จึงมีบ่อยครั้งที่มีการหยิบยกเนื้อหาในรายการนี้ไปถกเถียงกันในสือกระแสหลักและสือออนไลน์อยู่บ่อยครั้ง ดังเช่นกรณีประเด็นของ จ้ะ คันหู [1] และกรณีความไม่เหมาะในคำสอนของแม่ชีทศพรที่เปรียบเทียบอวัยวะเพศหญิงกับประตูเมืองและคำสอนแก้เคล็ดโดยแนะนำให้ลูกศิษย์ร่วมเพศกัน [2]
รายชื่อตอนที่ออกอากาศ[แก้]
| ตอนที่ | วันออกอากาศ | ชื่อตอน |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 กุมภาพันธ์ 2554 | มุมมองของปัญหาการทำแท้ง[2] |
| 2 | 13 กุมภาพันธ์ 2554 | ปัญหาการแต่งงานของคนรักร่วมเพศ และคำถามว่าเกย์คืออะไร?[3] |
| 3 | 20 กุมภาพันธ์ 2554 | ยืนตรงเคารพธงเพลงชาติเพื่ออะไร[4] |
| 4 | 27 กุมภาพันธ์ 2554 | โฆษณา เครื่องดื่มขาวอมชมพู สะท้อนความไร้การศึกษาวงการโฆษณาไทย[5] |
| 5 | 6 มีนาคม 2554 | 'ชาตินี้' หรือ 'ชาติไหน' ที่วัฒนธรรมแบบไทยจะผงาดสู่เวทีโลก[6] |
| 6 | 13 มีนาคม 2554 | เครื่องแบบนักเรียน " มีอยู่" หรือ "ยกเลิก" ?[7] |
| 7 | 20 มีนาคม 2554 | I love Hitler[8] |
| 8 | 27 มีนาคม 2554 | “Sex toy” บาปแห่งการช่วยตัวเอง[9] |
| 9 | 3เมษายน 2554 | จิ๋มเอื้ออาทร-เฉาะฟรี-สตรีข้ามเพศ[10] |
| 10 | 10 เมษายน 2554 | คำผกา แฉ! สแกนกรรม แม่ชีทศพร[11] |
| 11 | 17 เมษายน 2554 | คนไทย จำเป็นหรือไม่ ต้องมี 'บัตรประชาชน'[12] |
| 12 | 24 เมษายน 2554 | อาการแพ้นม ของสังคมไทย (ตอน 1)[13] |
| 13 | 1 พฤษภาคม 2554 | อาการแพ้นม ของสังคมไทย (ตอน 2)[14] |
| 14 | 8 พฤษภาคม 2554 | 'ละครน้ำเน่า'[15] |
| 15 | 15 พฤษภาคม 2554 | จาก 'ลัดดา' ถึง 'เรยา' และ 'ชั่วฟ้าดินสลาย'[16] |
| 16 | 22 พฤษภาคม 2554 | การปรับตัวของราชวงศ์อังกฤษ จะเลือก'กระฎุมพี'หรือ'เซเลบบริตี้'[17] |
| 17 | 29 พฤษภาคม 2554 | ปริญญาบัตร วัดการศึกษาได้จริงหรือ?[18] |
| 18 | 5 มิถุนายน 2554 | เมื่อ 'ผู้หญิง' ก้าวเข้ามาในพื้นที่ของผู้ชาย[19] |
| 19 | 12 มิถุนายน 2554 | แน่ใจหรือว่า อยากอยู่แบบภูฏาน ?[20] |
| 20 | 19 มิถุนายน 2554 | ประวัติศาสตร์การรับน้องและระบบ Sotus ในประเทศไทย[21] |
| 21 | 26 มิถุนายน 2554 | ประวัติศาสตร์การรับน้องและระบบ Sotus ในประเทศไทย (ตอนจบ)[22] |
| 22 | 3 กรกฎาคม 2554 | นิตยสารเกย์ ในเมืองไทย[23] |
| 23 | 10 กรกฎาคม 2554 | กรุงเทพฯ มหานครแห่งการอ่าน[24] |
| 24 | 17 กรกฎาคม 2554 | พิษตกค้างหลังการเลือกตั้ง[25] |
| 25 | 24 สิงหาคม 2554 | พิษตกค้างการเมืองหลังการเลือกตั้ง (ตอนจบ)[26] |
| 26 | 31 กรกฎาคม 2554 | วัฒนธรรมไทย กับดีไซน์ คัลเจอร์[27] |
| 27 | 7 สิงหาคม 2554 | แคมเปญ รณรงค์เลิกเหล้า[28] |
| 28 | 14 สิงหาคม 2554 | แคมเปญ รณรงค์เลิกเหล้า ตอน 2[29] |
| 29 | 21 สิงหาคม 2554 | Slut walk[30] |
| 30 | 28 สิงหาคม 2554 | อารมณ์หรือเหตุผล ในกระบวนการยุติธรรม[31] |
| 31 | 3 กันยายน 2554 | แฟชั่นกับผู้นำหญิง[32] |
| 32 | 4 กันยายน 2554 | กินเนื้อหมาหรือเลี้ยงสุนัข[33] |
| 33 | 10 กันยายน 2554 | กินเนื้อหมาหรือเลี้ยงสุนัข ตอน 2[34] |
| 34 | 11 กันยายน 2554 | “สัปปายะสภาสถาน” แบบรัฐสภาใหม่ของไทย[35] |
| 35 | 17 กันยายน 2554 | การคุกคามสื่อ & คู่มือการเลี้ยงลูก[36] |
| 36 | 18 กันยายน 2554 | คำผกา "คันหู"[37] |
| 37 | 24 กันยายน 2554 | คิดเล่นเห็นต่างกับคำผกา Special in Chiang Mai[38] |
| 38 | 25 กันยายน 2554 | คิดเล่นเห็นต่างกับคำผกา Special in Chiang Mai (ตอนจบ)[39] |
| 39 | 1 ตุลาคม 2554 | ปัญหาเกย์วัยรุ่นฆ่าตัวตาย กับโครงการ It Gets Better [40] |
| 40 | 2 ตุลาคม 2554 | ชุดประจำชาติไทยในฐานะประเพณีประดิษฐ์ [41] |
| 41 | 8 ตุลาคม 2554 | ชุดประจำชาติไทยในฐานะประเพณีประดิษฐ์(ตอบจบ) [42] |
| 42 | 9 ตุลาคม 2554 | พาเหรดนาซี และ ปัญหาแบบเรียนประวัติศาสตร์ของเด็กไทย [43] |
| 43 | 15 ตุลาคม 2554 | ความเข้มแข็งของวัฒนธรรมการอ่านในสังคมไทย [44] |
| 44 | 16 ตุลาคม 2554 | น้ำท่วมและน้ำใจของคนไทย [45] |
| 45 | 16 ตุลาคม 2554 | คำถาม?... หลังจากน้ำลด [46] |
| 46 | 23 ตุลาคม 2554 | เป็นกะเทย เป็นแล้วหายได้จริงหรือ? [47] |
| 47 | 29 ตุลาคม 2554 | “วัฒนธรรมวาย” ที่ไม่ใช่เหล้าองุ่น แต่เป็นวายในงานวรรณกรรม [48] |
| 48 | 30 ตุลาคม 2554 | ถึงเวลาหรือยัง ? ที่"โสเภณี" จะเป็นอาชีพถูกกฎหมาย [49] |
อ้างอิง[แก้]
แหล่งข้อมูลอื่น[แก้]
- เว็บทางการของรายการคิดเล่นเห็นต่างกับคำผกา
- โอ๊คแจ้ง..วอยซ์ทีวี พร้อมเสิร์ฟ 3 รายการใหม่ 3 รสชาติ คุณปลื้มนำทีมเด็ดทุกช่วง
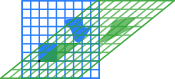
m = 1.25 horizontal shear
In mathematics, shear mapping or transvection is a particular kind of linear mapping. Linear mapping is a function between two vector spaces that preserves the operations of vector addition and scalar multiplication. A shear mapping's effect leaves all points on one axis fixed, while the other points are shifted parallel to the axis by a distance proportional to their perpendicular distance from that axis.
Shear mappings carry areas into equal areas and volumes into equal volumes, as they preserve the width, length, and etc. of parallelograms; see equi-areal mapping for the reason and for other linear mappings that have this property.
Elementary form[แก้]
In the plane {(x, y): x,y ∈ R }, a horizontal shear (or shear parallel to the x axis) is represented by the linear mapping
This leaves horizontal lines y = c invariant, but for m ≠ 0 maps vertical lines x = a into lines y' = (x' − a)/m having slope 1/m
Substituting 1/m for m in the matrix gives lines y = m(x − a) of slope m, if desired.
A vertical shear (or shear parallel to the y axis) of lines is accomplished by the linear mapping
The vertical shear leaves vertical lines x = a invariant, but maps horizontal lines y = b into lines y' = mx' + b
The matrices above are special cases of shear matrices, which allow for generalization to higher dimensions. The shear elements here are either m or 1/m, case depending.
The following applications of shear mapping were noted by William Kingdon Clifford:
- "A succession of shears will enable us to reduce any figure bounded by straight lines to a triangle of equal area."
- "... we may shear any triangle into a right-angled triangle, and this will not alter its area. Thus the area of any triangle is half the area of the rectangle on the same base and with height equal to the perpendicular on the base from the opposite angle."
The area-preserving property of a shear mapping can be used for results involving area. For instance, the Pythagorean theorem has been illustrated with shear mapping (see external link).
Advanced form[แก้]
For a vector space V and subspace W, a shear fixing W translates all vectors parallel to W.
To be more precise, if V is the direct sum of W and W′, and we write vectors as
- v = w + w′
correspondingly, the typical shear fixing W is L where
- L(v) = (w + Mw′) + w ′
where M is a linear mapping from W′ into W. Therefore in block matrix terms L can be represented as
with blocks on the diagonal I (identity matrix), with M above the diagonal, and 0 below.
References[แก้]
- William Kingdon Clifford (1885) Common Sense and the Exact Sciences, page 113.
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Shear" from Mathworld, A Wolfram Web Resource.
- Mike May S.J. Pythagorean theorem by shear mapping Saint Louis University website; requires Java and Geogebra. Click on the "Steps" slider and observe shears at steps 5 and 6.
- CS1 errors: extra text: edition
- Year of birth missing (living people)
- Living people
- Roboticists
- Canadian scientists
- WowWee
- Stability theory
- 1912 births
- 1988 deaths
- American people of Italian descent
- Control theorists
- Systems templates
- Technology and applied science templates
- NA-Class Systems articles
- 1930 births
- People from Budapest
- Hungarian mathematicians
- Hungarian engineers
- Hungarian electrical engineers
- Hungarian scientists
- Members of the United States National Academy of Sciences
- Members of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences
- Members of the French Academy of Sciences
- 20th-century mathematicians
- Columbia University alumni
- Columbia Engineering alumni
- ETH Zurich faculty
- IEEE Medal of Honor recipients
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology alumni
- Stanford University faculty
- Systems engineers
- University of Florida faculty
- Richard E. Bellman Control Heritage Award recipients
- IEEE Centennial Medal laureates
- Complex analysis
- Dynamical systems
- ประเภทของฟังก์ชัน
- Mathematical terminology
- รายการโทรทัศน์ไทย
- Functions and mappings
- พีชคณิตเชิงเส้น
- Transformation (function)
- Affine geometry












































