ยูเจนอล
| |

| |
| ชื่อ | |
|---|---|
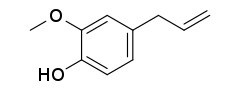
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Methoxy-4-(prop-2-en-1-yl)phenol | |
ชื่ออื่น
| |
| เลขทะเบียน | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1366759 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| เคมสไปเดอร์ | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.355 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
ผับเคม CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| คุณสมบัติ | |
| C10H12O2 | |
| มวลโมเลกุล | 164.204 g·mol−1 |
| ความหนาแน่น | 1.06 g/cm3 |
| จุดหลอมเหลว | −7.5 องศาเซลเซียส (18.5 องศาฟาเรนไฮต์; 265.6 เคลวิน) |
| จุดเดือด | 254 องศาเซลเซียส (489 องศาฟาเรนไฮต์; 527 เคลวิน) |
| pKa | 10.19 at 25 °C |
| −1.021×10−4 cm3/mol | |
| ความหนืด |
|
| ความอันตราย | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| จุดวาบไฟ | 104 องศาเซลเซียส (219 องศาฟาเรนไฮต์; 377 เคลวิน) |
| สารประกอบอื่นที่เกี่ยวข้องกัน | |
สารประกอบที่เกี่ยวข้อง
|
2-Phenethyl propionate |
หากมิได้ระบุเป็นอื่น ข้อมูลข้างต้นนี้คือข้อมูลสาร ณ ภาวะมาตรฐานที่ 25 °C, 100 kPa
| |

ยูเจนอล หรือ ยูจีนอล (อังกฤษ: Eugenol; ipa: /ˈjuːdʒɪnɒl/)(C10H12O2) หรือเรียกชื่อตามระบบ IUPAC ว่า 2-เมทอกซี-4-(2-โพรพินิล)ฟีนอล เป็นสารประกอบไควอะคอลที่มีสายโซ่อะลิล และเป็นสมาชิกของกลุ่มสารเคมีที่เรียกว่าอัลลิลเบนซีน[2] ซึ่งเป็นของเหลวมันที่มีกลิ่นหอม ตั้งแต่สีใสจนถึงสีเหลืองอ่อน สกัดได้จากน้ำมันหอมระเหยบางชนิด โดยเฉพาะจากกานพลู จันทน์เทศ อบเชย โหระพา และใบกระวาน[3][4][5][6] มีความเข้มข้นของยูจีนอลในน้ำมันกานพลูมีประมาณ 80–90% และในน้ำมันใบกานพลูประมาณ 82–88%[7] ยูจีนอลมีกลิ่นหอมเผ็ดคล้ายกลิ่นกานพลู[8] ซึ่งชื่อยูจีนอลนี้มีที่มาจาก Eugenia caryophyllata ซึ่งเป็นชื่อทางวิทยาศาสตร์ของกานพลูตามการจำแนกในสมัยของลินเนียส แต่ปัจจุบันชื่อที่ได้รับการยอมรับคือ Syzygium aromaticum[9]
การนำไปใช้
[แก้]เป็นของเหลวคล้ายน้ำมันสีเหลืองอ่อน ละลายได้เล็กน้อยในน้ำ ละลายได้ดีในตัวทำละลายอินทรีย์ มีกลิ่นคล้ายกานพลู มีประโยชน์ดังนี้
- ใช้ทำน้ำหอม
- ใช้แต่งกลิ่น
- ในทางการแพทย์ ยาฆ่าเชื้อ และระงับความรู้สึกเฉพาะที่
- ใช้ผลิตไอโซยูเจนอล (isoeugenol) เพื่อนำไปใช้ผลิตวานิลลิน (vanillin)
- เมื่อผสมกับสังกะสีออกไซด์ (zinc oxide) จะได้ซีเมนต์ที่ใช้ในงานทันตกรรม
- ใช้ผลิตสเตบิไลเซอร์ (stabilizers) และสารต้านอนุมูลอิสระ (antioxidant) ในงานผลิตพลาสติกและยาง
การได้ยาเกินขนาด
[แก้]การได้ยาเกินขนาดจะมีอาการดังนี้
- เลือดออกในปัสสาวะ
- วิงเวียนศีรษะ (dizziness)
- ชัก (convulsion)
- ท้องร่วง (diarrhea)
- หมดสติ (unconsciousness)
- หัวใจเต้นเร็ว (heartbeat)
การพบในธรรมชาติ
[แก้]ยูจีนอลเกิดขึ้นตามธรรมชาติในพืชหลายชนิด รวมถึงพืชต่อไปนี้:
- กานพลู (Syzygium aromaticum)[10][11][12]
- โกฐจุฬาลัมพา[ต้องการอ้างอิง]
- อบเชย[11][13]
- ใบกระวานอินเดีย[14]
- จันทน์เทศ (Myristica fragrans)[15]
- Ocimum basilicum (โหระพา)[16]
- Ocimum gratissimum (ใบยี่หร่า)[17][18]
- Ocimum tenuiflorum (ชื่อพ้อง Ocimum sanctum; ชื่อสามัญ กะเพรา)
- โป๊ยกั๊กญี่ปุ่น[19]
- สะระแหน่[20]
- ผักชีลาว[ต้องการอ้างอิง]
- Pimenta dioica (ออลสไปซ์) [ต้องการอ้างอิง]
- วะนิลา[ต้องการอ้างอิง]
- ใบกระวาน[ต้องการอ้างอิง]
- ขึ้นฉ่าย[ต้องการอ้างอิง]
- ขิง[ต้องการอ้างอิง]
ดูเพิ่มเติม
[แก้]เชิงอรรถและรายการอ้างอิง
[แก้]- ↑ Bingham EC, Spooner LW (1932). "The Fluidity Method for the Determination of Association. I". Journal of Rheology. 3 (2): 221–244. Bibcode:1932JRheo...3..221B. doi:10.1122/1.2116455. ISSN 0097-0360.
- ↑ "Eugenol". PubChem, US National Library of Medicine. 16 October 2021. สืบค้นเมื่อ 24 October 2021.
- ↑ "Constituents of the essential oil from leaves and buds of clove (Syzigium caryophyllatum L.) Alston" (PDF). Bangladesh Council of Scientific and Industrial Research BCSIR Laboratories. 4: 451–454.
- ↑ Mallavarapu GR, Ramesh S, Chandrasekhara RS, Rajeswara Rao BR, Kaul PN, Bhattacharya AK (1995). "Investigation of the essential oil of cinnamon leaf grown at Bangalore and Hyderabad". Flavour and Fragrance Journal. 10 (4): 239–242. doi:10.1002/ffj.2730100403.
- ↑ Yield and Oil Composition of 38 Basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) Accessions Grown in Mississippi เก็บถาวร 15 ตุลาคม 2010 ที่ เวย์แบ็กแมชชีน
- ↑ "Typical G.C. for bay leaf oil". Thegoodscentscompany.com. คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 17 March 2014. สืบค้นเมื่อ 2014-04-27.
- ↑ Barnes J, Anderson LA, Phillipson JS (2007) [1996]. Herbal Medicines (PDF) (3rd ed.). London: Pharmaceutical Press. ISBN 978-0-85369-623-0. คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิม (PDF)เมื่อ 1 July 2018. สืบค้นเมื่อ 27 April 2015.
- ↑ แม่แบบ:Cite HMDB
- ↑ Cortés Rojas DF, de Souza CR, Oliveira WP (February 2014). "Clove (Syzygium aromaticum): a precious spice". Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine. 4 (2): 90–6. doi:10.1016/S2221-1691(14)60215-X. PMC 3819475. PMID 25182278.
- ↑ Pathak SB, Niranjan K, Padh H, Rajani M (2004). "TLC Densitometric Method for the Quantification of Eugenol and Gallic Acid in Clove". Chromatographia. 60 (3–4): 241–244. doi:10.1365/s10337-004-0373-y. S2CID 95396304.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Bullerman LB, Lieu FY, Seier SA (July 1977). "Inhibition of growth and aflatoxin production by cinnamon and clove oils. Cinnamic aldehyde and eugenol". Journal of Food Science. 42 (4): 1107–1109. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.1977.tb12677.x.
- ↑ Lee K, Shibamoto T (2001). "Antioxidant property of aroma extract isolated from clove buds [Syzygium aromaticum (L.) Merr. et Perry]". Food Chemistry. 74 (4): 443–448. doi:10.1016/S0308-8146(01)00161-3.
- ↑ Kreydiyyeh SI, Usta J, Copti R (September 2000). "Effect of cinnamon, clove and some of their constituents on the Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase activity and alanine absorption in the rat jejunum". Food and Chemical Toxicology. 38 (9): 755–62. doi:10.1016/S0278-6915(00)00073-9. PMID 10930696.
- ↑ Dighe VV, Gursale AA, Sane RT, Menon S, Patel PH (2005). "Quantitative Determination of Eugenol from Cinnamomum tamala Nees and Eberm. Leaf Powder and Polyherbal Formulation Using Reverse Phase Liquid Chromatography". Chromatographia. 61 (9–10): 443–446. doi:10.1365/s10337-005-0527-6. S2CID 97399632.
- ↑ Bennett A, Stamford IF, Tavares IA, Jacobs S, Capasso F, Mascolo N, และคณะ (1988). "The biological activity of eugenol, a major constituent of nutmeg (..Myristica fragrans..): Studies on prostaglandins, the intestine and other tissues". Phytotherapy Research. 2 (3): 124–130. doi:10.1002/ptr.2650020305. S2CID 85114864.
- ↑ Johnson CB, Kirby J, Naxakis G, Pearson S (1999). "Substantial UV-B-mediated induction of essential oils in sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.)". Phytochemistry. 51 (4): 507–510. Bibcode:1999PChem..51..507J. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(98)00767-5.
- ↑ อ้างอิงผิดพลาด: ป้ายระบุ
<ref>ไม่ถูกต้อง ไม่มีการกำหนดข้อความสำหรับอ้างอิงชื่อGupta - ↑ Nakamura CV, Ueda-Nakamura T, Bando E, Melo AF, Cortez DA, Dias Filho BP (September 1999). "Antibacterial activity of Ocimum gratissimum L. essential oil". Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz. 94 (5): 675–8. doi:10.1590/S0074-02761999000500022. PMID 10464416.
- ↑ Ize-Ludlow D, Ragone S, Bruck IS, Bernstein JN, Duchowny M, Peña BM (November 2004). "Neurotoxicities in infants seen with the consumption of star anise tea". Pediatrics. 114 (5): e653-6. doi:10.1542/peds.2004-0058. PMID 15492355.
- ↑ "Lemon balm". University of Maryland Medical Center. คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 1 August 2013. สืบค้นเมื่อ 2020-12-07.


