ทะเลสาบฮูรอน
หน้าตา
| ทะเลสาบฮูรอน | |
|---|---|
 ชายฝั่งทะเลสาบฮูรอนในคาบสมุทรบรูซ | |
 | |
| ที่ตั้ง | อเมริกาเหนือ |
| กลุ่ม | เกรตเลกส์ |
| พิกัด | 44°48′N 82°24′W / 44.8°N 82.4°W |
| ชนิดของทะเลสาบ | น้ำแข็ง |
| ชื่อในภาษาแม่ | |
| แหล่งน้ำไหลเข้าหลัก | ช่องแคบแมคคิแนค, แม่น้ำเซนต์แมรี |
| แหล่งน้ำไหลออก | แม่น้ำเซนต์แคลร์ |
| พื้นที่รับน้ำ | 51,700 ตารางไมล์ (134,000 ตารางกิโลเมตร)[8] |
| ประเทศในลุ่มน้ำ | แคนาดา และสหรัฐ |
| ช่วงยาวที่สุด | 206 ไมล์ (332 กิโลเมตร)[8] |
| ช่วงกว้างที่สุด | 183 ไมล์ (295 กิโลเมตร)[8] |
| พื้นที่พื้นน้ำ | 23,007 ตารางไมล์ (59,590 ตารางกิโลเมตร)[8] |
| ความลึกโดยเฉลี่ย | 195 ฟุต (59 เมตร)[8] |
| ความลึกสูงสุด | 750 ฟุต (229 เมตร)[8] |
| ปริมาณน้ำ | 850 ลูกบาศก์ไมล์ (3,543 ลูกบาศก์กิโลเมตร)[8] |
| เวลาพักน้ำ | 22 ปี |
| ความยาวชายฝั่ง1 | 1,850 ไมล์ (2,980 กิโลเมตร) plus 1,980 ไมล์ (3,190 กิโลเมตร) for islands[9] |
| ความสูงของพื้นที่ | 577 ฟุต (176 เมตร)[8] |
| เกาะ | เกาะแมนิทูลิน |
| ส่วนย่อยลุ่มน้ำ | Georgian Bay, North Channel |
| เมือง | Bay City, Alpena, Cheboygan, St. Ignace, Port Huron ในรัฐมิชิแกน; Goderich, Sarnia, Owen Sound ในรัฐออนแทรีโอ |
| อ้างอิง | [10] |
| 1 ความยาวแนวชายฝั่งไม่ได้ถูกวัดอย่างละเอียด | |

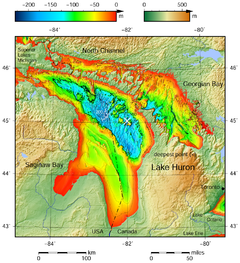
ทะเลสาบฮูรอน หรือ ทะเลสาบฮิวรอน (อังกฤษ: Lake Huron; ฝรั่งเศส: Lac Huron) เป็นทะเลสาบหนึ่งในหมู่ทะเลสาบทั้งห้า (เกรตเลกส์) ในทวีปอเมริกาเหนือ เป็นพรมแดนธรรมชาติระหว่างรัฐมิชิแกนของสหรัฐอเมริกากับรัฐออนแทริโอของแคนาดา มีพื้นน้ำรวมทั้งสิ้น 59,600 ตารางกิโลเมตร ความลึกสุดที่ 230 เมตร ความลึกเฉลี่ย 59 เมตร ชายฝั่งยาว 6,156 กิโลเมตร [11]
อ้างอิง
[แก้]- ↑ National Geophysical Data Center (1999). "Bathymetry of Lake Erie and Lake Saint Clair". National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration. doi:10.7289/V5KS6PHK. สืบค้นเมื่อ March 23, 2015. (only small portion of this map)
- ↑ National Geophysical Data Center (1999). "Bathymetry of Lake Huron". National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration. doi:10.7289/V5G15XS5. สืบค้นเมื่อ March 23, 2015.
- ↑ National Geophysical Data Center (1996). "Bathymetry of Lake Michigan". National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration. doi:10.7289/V5B85627. สืบค้นเมื่อ March 23, 2015. (only small portion of this map)
- ↑ National Geophysical Data Center (1999). "Bathymetry of Lake Ontario". National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration. doi:10.7289/V56H4FBH. สืบค้นเมื่อ March 23, 2015. (only small portion of this map)
- ↑ National Geophysical Data Center (1999). "Bathymetry of Lake Superior". National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration. สืบค้นเมื่อ March 23, 2015.
(the general reference to NGDC because this lake was never published, compilation of Great Lakes Bathymetry at NGDC has been suspended). (only small portion of this map) - ↑ Hastings, D.; Dunbar, P.K. (1999). "Global Land One-kilometer Base Elevation (GLOBE) v.1". National Geophysical Data Center, National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration. doi:10.7289/V52R3PMS. สืบค้นเมื่อ March 16, 2015.
- ↑ "About Our Great Lakes: Tour". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) - Great Lakes Environmental Research Laboratory (GLERL). คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ May 5, 2011. สืบค้นเมื่อ April 2, 2015. Google Earth Great Lakes Tour (Map). คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ January 5, 2015.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 8.6 8.7 "Great Lakes Factsheet No. 1". U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. June 25, 2012. สืบค้นเมื่อ March 6, 2014.
- ↑ "Shorelines of the Great Lakes". Michigan Department of Environmental Quality. คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ April 5, 2015.
- ↑ Wright, John W., บ.ก. (2006). The New York Times Almanac (2007 ed.). New York: Penguin Books. p. 64. ISBN 0-14-303820-6 – โดยทาง Archive.org.
- ↑ Wright, John W. (ed.) ; Editors and reporters of The New York Times (2006). The New York Times Almanac, 2007, New York, New York: Penguin Books, 64. ISBN 0-14-303820-6.
แหล่งข้อมูลอื่น
[แก้]วิกิมีเดียคอมมอนส์มีสื่อที่เกี่ยวข้องกับ ทะเลสาบฮูรอน
- EPA's Great Lakes Atlas
- สายพันธุ์ปลาในทะเลสาบฮูอน เก็บถาวร 2008-02-06 ที่ เวย์แบ็กแมชชีน
- สำรวจชายฝั่งทะเลสาบ
- Lake Huron Binational Partnership Action Plan
- ข้อมลทะเลสาบฮูรอน เก็บถาวร 2005-05-15 ที่ เวย์แบ็กแมชชีน
- Lake Huron GIS เก็บถาวร 2007-03-10 ที่ เวย์แบ็กแมชชีน
- Michigan DNR map of Lake Huron
- ประภาคาร
- Bibliography on Michigan lighthouses เก็บถาวร 2008-05-31 ที่ เวย์แบ็กแมชชีน
- Interacitvew map of lighthouses, Georgian Bay, Lake Huron เก็บถาวร 2008-06-11 ที่ เวย์แบ็กแมชชีน
- Interactive map of lighthouses in North and East Lake Huron เก็บถาวร 2008-06-11 ที่ เวย์แบ็กแมชชีน
- Interactive map of lighthouses in North and West Lake Huron เก็บถาวร 2008-04-25 ที่ เวย์แบ็กแมชชีน
- Terry Pepper on lighthouses of the Western Great Lakes เก็บถาวร 2008-01-30 ที่ เวย์แบ็กแมชชีน
- Wagner, John L., Beacons Shining in the Night, บรรณานุกรมประภาคารในมิชิแกน, ความเป็นมา, ประวัติศาสตร์, ภาพถ่าย,ห้องสมุดประวัติศาสตร์ Clarke, หอสมุดกลางมหาวิทยาลัยมิชิแกน