โครโมโซมคู่เหมือน
หน้าตา
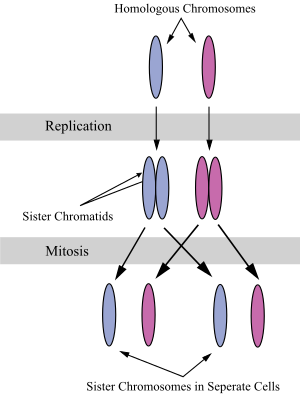
โครโมโซมคู่เหมือน (อังกฤษ: homologous chromosomes, homologs) คือคู่ของโครโมโซมที่เซลล์ได้รับมาจากฝั่งพ่อและฝั่งแม่และมาจับคู่กันในขั้นตอนการปฏิสนธิ มียีนเดียวกันในตำแหน่งเดียวกันของโครโมโซม ทำให้โครโมโซมคู่เหมือนนี้สามารถจับคู่กันได้พอดีก่อนที่จะแยกกันในกระบวนการแบ่งเซลล์แบบไมโอซิส
โครโมโซมคู่เหมือนมีตำแหน่งของยีนตรงกัน แต่ไม่ได้มีลำดับเบสเหมือนกันทุกประการ ถือเป็นผลผลิตจากการปฏิสนธิ และอาจถือเป็นภาวะปกติของเซลล์สิ่งมีชีวิต ต่างจากโครโมโซมคู่พี่น้องซึ่งเป็นการทำซ้ำโครโมโซมอันเดิม ด้วยกระบวนการการถ่ายแบบดีเอ็นเอเพื่อเตรียมแบ่งเซลล์แบบไมโทซิส ซึ่งมีลำดับเบสเหมือนกันทุกประการ[1]
อ้างอิง
[แก้]- ↑ Pollard TD, Earnshaw WC, Lippincott-Schwartz J (2008). Cell Biology (2 ed.). Philadelphia: Saunders/Elsevier. pp. 815, 821–822. ISBN 1-4160-2255-4.
