ผลต่างระหว่างรุ่นของ "ปากแหว่งเพดานโหว่"
ล อ้างอิง |
|||
| บรรทัด 71: | บรรทัด 71: | ||
== แหล่งข้อมูลอื่น == |
== แหล่งข้อมูลอื่น == |
||
{{Commonscat|Cleft lip}} |
{{Commonscat|Cleft lip}} |
||
* [http://161.200.102.195/hospital/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=25&Itemid=41 โครงการศัลยกรรมตกแต่งแก้ไขปากแหว่ง-เพดานโหว่เฉลิมพระเกียรติฯ โรงพยาบาลจุฬาลงกรณ์] |
|||
* [http://www.childrenshospital.org/az/Site2034/mainpageS2034P0.html Cleft lip and palate - Children's Hospital Boston] |
* [http://www.childrenshospital.org/az/Site2034/mainpageS2034P0.html Cleft lip and palate - Children's Hospital Boston] |
||
รุ่นแก้ไขเมื่อ 01:33, 24 มีนาคม 2552
| ปากแหว่งเพดานโหว่ (Cleft lip and palate) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| บัญชีจำแนกและลิงก์ไปภายนอก | |
| ICD-10 | Q35-Q37 |
| ICD-9 | 749 |
| DiseasesDB | 29604 29414 |
| eMedicine | ped/2679 |
ปากแหว่ง (อังกฤษ: cleft lip; ละติน: cheiloschisis) และเพดานโหว่ (อังกฤษ: cleft palate; ละติน: palatoschisis) หรือมักเรียกรวมกันว่าปากแหว่งเพดานโหว่ เป็นความผิดปกติแต่กำเนิดของการเจริญของใบหน้าระหว่างการตั้งครรภ์ การรักษาผู้ป่วยที่พิการปากแหว่งเพดานโหว่ทำโดยการผ่าตัดทันทีหลังคลอด อัตราผู้ป่วยปากแหว่งเพดานโหว่เกิดราว 1 ในทารกแรกเกิด 600-800 คน
ปากแหว่ง
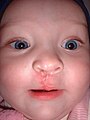
ถ้ารอยแยกนั้นไม่ถึงส่วนเพดานปาก จะเรียกความผิดปกตินี้ว่า ปากแหว่ง หากเกิดที่ด้านบนของริมฝีปากในลักษณะช่องว่างเล็กๆ หรือเว้าเล็กน้อยเรียกว่า ปากแหว่งไม่สมบูรณ์ หรือปากแหว่งบางส่วน (partial or incomplete cleft) แต่หากรอยแยกนี้ต่อเนื่องไปถึงจมูกเรียกว่า ปากแหว่งสมบูรณ์ (complete cleft) ปากแหว่งอาจเกิดข้างเดียวหรือสองข้างก็ได้ ปากแหว่งมีสาเหตุจากการเชื่อมของขากรรไกรบนและส่วนยื่นจมูกด้านใกล้กลาง (medial nasal processes) เพื่อเป็นเพดานปากปฐมภูมิ (primary palate) ไม่สมบูรณ์
-
ปากแหว่งข้างเดียวไม่สมบูรณ์ (Unilateral incomplete)
-
ปากแหว่งข้างเดียวสมบูรณ์ (Unilateral complete)
-
ปากแหว่งสองข้างสมบูรณ์ (Bilateral complete)
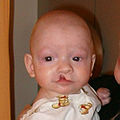
ปากแหว่งรูปแบบหนึ่งเรียกว่า microform cleft ซึ่งมีความรุนแรงน้อยกว่า มีลักษณะเป็นรอยเล็กๆ บนริมฝีปากหรือมีลักษณะคล้ายแผลเป็นจากริมฝีปากไปยังจมูก ในบางรายกล้ามเนื้อหูรูดปากใต้แผลเป็นนั้นอาจผิดปกติซึ่งต้องได้รับการผ่าตัด ทารกที่เกิดมามีความผิดปกติดังกล่าวจำเป็นต้องได้รับการประเมินความรุนแรงจากแพทย์ด้านใบหน้าและปากทันที
-
เด็กชายอายุ 3 เดือนปากแหว่งข้างเดียวไม่สมบูรณ์ ก่อนได้รับการผ่าตัด
-
เด็กชายคนเดียวกัน 1 เดือนหลังจากผ่าตัด
-
เด็กชายคนเดียวกันอายุ 1 ปี 5 เดือน สังเกตว่าแผลเป็นจะดูจางลงตามอายุ
-
เด็กหญิงอายุ 6 เดือนปากแหว่งข้างเดียวสมบูรณ์ ก่อนได้รับการผ่าตัด
-
เด็กหญิงคนเดียวกัน 1 เดือนหลังจากผ่าตัด
-
เด็กหญิงคนเดียวกัน อายุ 5 ปี 4 เดือน สังเกตว่าแผลเป็นจะดูจางลงตามอายุ
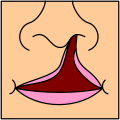
เพดานโหว่
เพดานโหว่ เป็นภาวะที่แผ่นกระดูกของกะโหลกศีรษะ 2 แผ่นไม่เชื่อมกันเป็นเพดานแข็ง อาจมีช่องโหว่ของเพดานอ่อนได้ด้วยเช่นกัน ผู้ป่วยส่วนมากมักมีปากแหว่งร่วมด้วย เพดานโหว่เกิดราว 1 ในทารกแรกเกิดมีชีพ 700 คนทั่วโลก[1]
Palate cleft can occur as complete (soft and hard palate, possibly including a gap in the jaw) or incomplete (a 'hole' in the roof of the mouth, usually as a cleft soft palate). When cleft palate occurs, the uvula is usually split. It occurs due to the failure of fusion of the lateral palatine processes, the nasal septum, and/or the median palatine processes (formation of the secondary palate).
The hole in the roof of the mouth caused by a cleft connects the mouth directly to the nasal cavity.
Note: the next images show the roof of the mouth. The top shows the nose, the lips are colored pink. For clarity the images depict a toothless infant.
-
Incomplete cleft palate
-
Unilateral complete lip and palate
-
Bilateral complete lip and palate
A direct result of an open connection between the oral cavity and nasal cavity is velopharyngeal insufficiency (VPI). Because of the gap, air leaks into the nasal cavity resulting in a hypernasal voice resonance and nasal emissions.[2] Secondary effects of VPI include speech articulation errors (e.g., distortions, substitutions, and omissions) and compensatory misarticulations (e.g., glottal stops and posterior nasal fricatives).[3]. Possible treatment options include speech therapy, prosthetics, augmentation of the posterior pharyngeal wall, lengthening of the palate, and surgical procedures.[2]
Submucous cleft palate (SMCP) can also occur, which is an occult cleft of the soft palate with a classic clinical triad of bifid uvula, notching of the hard palate, and zona pellucida.
อ้างอิง
- ↑ "Statistics by country for cleft palate". WrongDiagnosis.com. สืบค้นเมื่อ 2007-04-24.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Sloan GM (2000). "Posterior pharyngeal flap and sphincter pharyngoplasty: the state of the art". Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 37 (2): 112–22. doi:10.1597/1545-1569 (2000) 037<0112:PPFASP>2.3.CO;2. PMID 10749049.
{{cite journal}}: ตรวจสอบค่า|doi=(help) - ↑ Hill, J.S. (2001). Velopharyngeal insufficiency: An update on diagnostic and surgical techniques. Current Opinion in Otolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery, 9, 365-368.